Figure 5. POU4F3nT+ cells in ventralized inner ear organoids express cochlear hair cell markers.
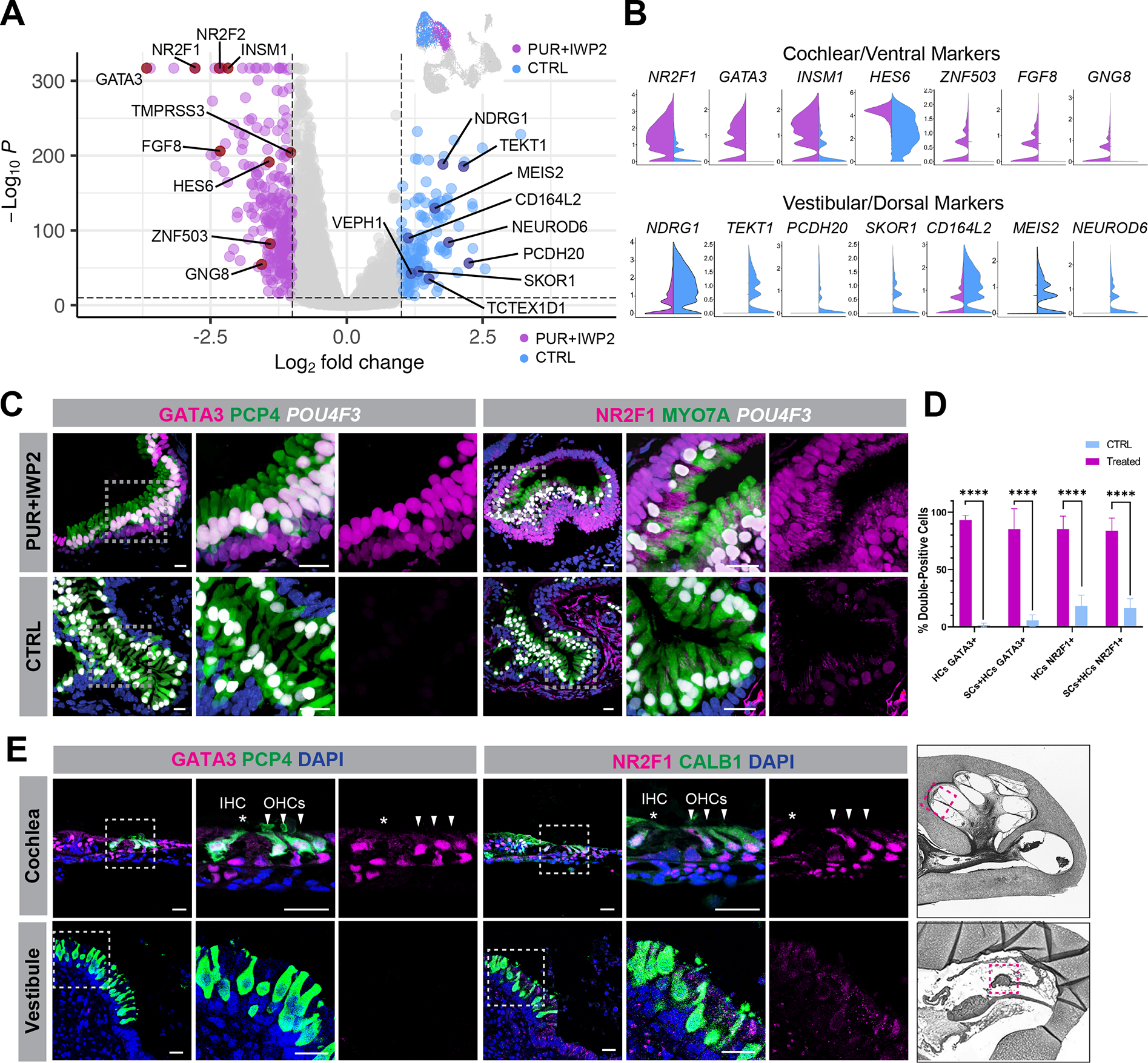
(A-B) Volcano plot (A) together with violin plots (B) confirm differentially expressed cochlear and vestibular hair cell marker genes between PUR+IWP2 and CTRL hair cells. Additionally, previously unrecognized genes, such as NR2F1, TMPRSS3, CD164L2, ZBBX and SKOR1, are differentially expressed between PUR+IWP2 and CTRL hair cells.
(C) Representative immunohistochemistry validates differential expression of NR2F1 and GATA3 between PUR+IWP2 and CTRL organoids.
(D) Comparison of the percentage of NR2F1- or GATA3-positive hair cells (HCs: POU4F3nT-labeled) and supporting cells (SCs: SOX2-labeled) in PUR+IWP2 vs. CTRL immunofluorescent images of inner ear organoids; n = 9 biological samples from separate experiments; Welch’s two-sided t-test ****P<0.000001; values are mean ± SEM.
(E) NR2F1 and GATA3 are expressed in cochlear hair cells, but absent in vestibular hair cells of the crista ampulla in the GW18 human inner ear.
Scale bars, 20 μm (C, E).
