Figure 7. A subpopulation of hair cells derived from ventralized organoids express PRESTIN and exhibit voltage-gated currents characteristic of cochlear outer hair cells.
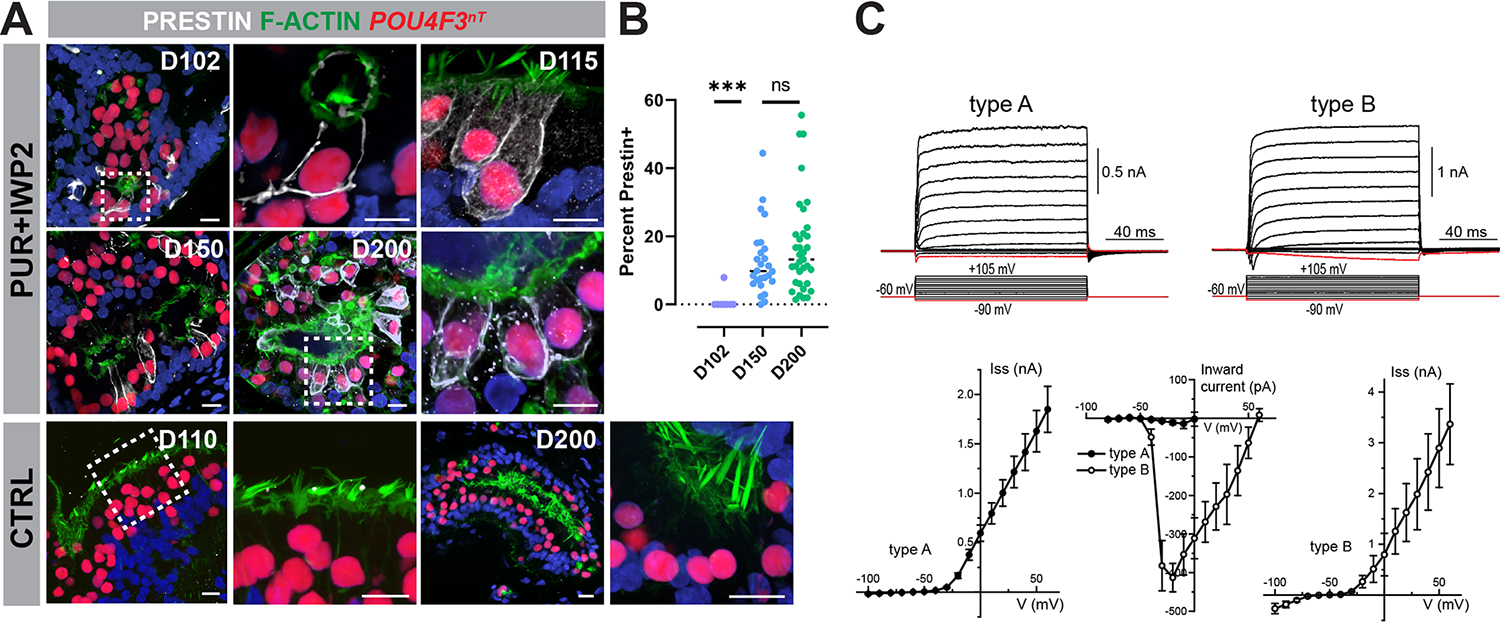
(A-B) PRESTIN+ hair cells increase over time in PUR+IWP2 inner ear organoids. Representative immunohistochemistry for PRESTIN in PUR+IWP2 samples at D102, −150, and −200, along with the comparison of the percentage of hair cells expressing PRESTIN among the different age groups, reveals an increasing number of hair cells expressing membranous PRESTIN over time in culture. In contrast, PRESTIN is undetectable in CTRL hair cells at D110 or −200.
(C) Voltage-gated currents in hESC-derived hair cells. Typical whole cell current responses (top traces) to the voltage step protocol (bottom traces) in type A and type B cells. Average steady-state current amplitude at the end of voltage step in type A and type B cells. The peak amplitude of the negative inward current. All data are shown as Mean ± Standard Error. Age of the cells: d138-d164.
Scale bars,10 μm (A).
