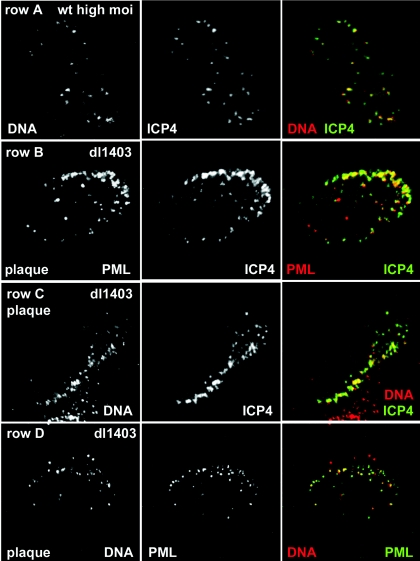
FIG. 1.
ICP4 foci that form at early times of HSV-1 infection are commonly associated with viral DNA. (Row A) Combined in situ hybridization of HSV-1 DNA and immunostaining of ICP4 in an HFFF-2 cell 3 h after infection with wt HSV-1 (MOI, 10 PFU/cell), showing DNA, ICP4, and merged (DNA is red, and ICP4 is green) images. (Row B) A HFFF-2 cell at the edge of a developing dl1403 plaque was stained for PML and ICP4 (red and green, respectively, in the merged image), demonstrating the association of PML foci with the ICP4 foci that characteristically form just inside the nuclear periphery. (Row C) The ICP4 foci that form just inside the nuclear periphery in cells at the edge of a developing plaque are extensively associated with DNA (ICP4 is green and DNA is red in the merged image). (Row D) In such cells, foci of viral DNA inside and close to the edge of the nucleus are commonly associated with structures containing PML (DNA is red and PML is green in the merged image).