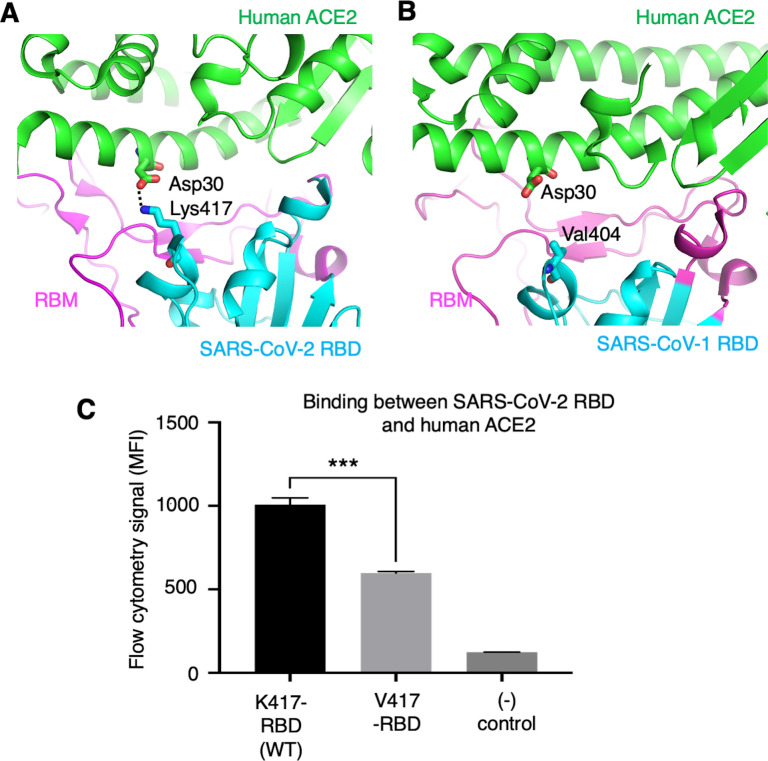
Figure 5. Role of residue 417 in direct interaction with ACE2 receptor.
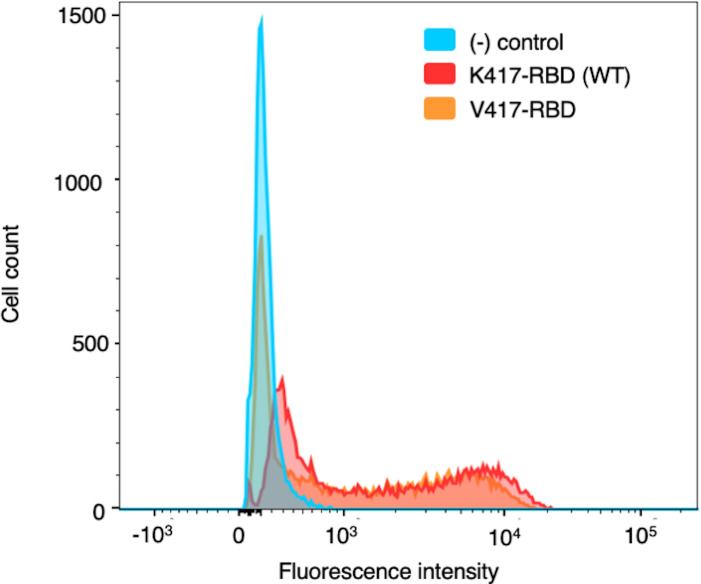
(A) Lys417 in SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) forms a favorable salt bridge with Asp30 in human ACE2. PDB code: 6M0J. (B) Val404 in SARS-CoV-1 RBD (whose position is equivalent to residue 417 in SARS-CoV-2 RBD) does not form any direct interaction with human ACE2. PDB code: 2AJF. (C) Flow cytometry assay to detect the interactions between recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RBD and cell-surface-anchored human ACE2 (Figure 5—source data 1). The RBD contains either Lys417 (wild-type residue) or Val417 (mutant residue). MFI: median fluorescence intensity. See Figure 5—figure supplement 1 for details of this experiment. Data are mean + SEM. A comparison (two-tailed Student’s t-test) was performed on data between indicated groups (n = 3). ***p<0.001. This experiment was repeated independently three times with similar results.