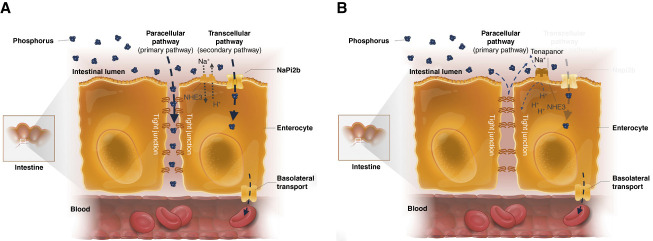
Figure 4.
Intestinal phosphate absorption pathways.2 (A) Intestinal phosphate absorption occurs through the transcellular and paracellular pathways. Absorption through the secondary transcellular pathway is facilitated by the sodium-dependent phosphate transporter NaPi2b. In the primary paracellular pathway, phosphate is absorbed passively along the concentration gradient through tight junctions. (B) Tenapanor reduces permeability of tight junctions to phosphate, reducing paracellular phosphate absorption. NaPi2b, sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2b; NHE3, sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3.