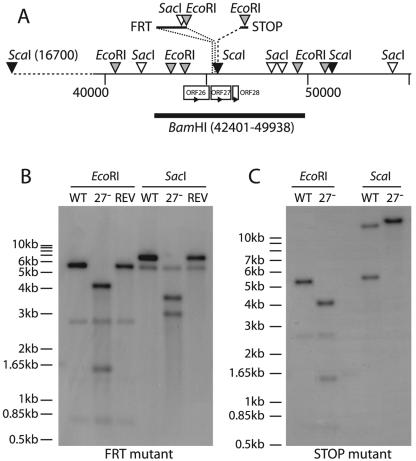
FIG. 3.
Disruption of ORF27 in the MHV-68 genome. (A) The sites of ORF27 mutagenesis are shown, as are relevant genomic and introduced restriction sites. Both mutations were located near the 5′ end of ORF27, downstream of the 3′ end of ORF26, and well upstream of the 5′ end of ORF28. The positions and orientations of the neighboring ORFs are shown. (B) The BamHI-C genomic fragment shown in panel A was used as a probe template for Southern blotting of viral DNA derived from the wild-type virus (WT), the ORF27− FRT mutant (27−), or its revertant (REV). The predicted fragments for WT viral DNA were 2,703, 744, 5,611, and 1,342 bp for EcoRI (the 1,342-bp band is very faint due to limited overlap with the probe) and 6,531, 372, and 5,553 bp for SacI. With the FRT mutation, the 5,611-bp EcoRI band was cut into 4,150- and 1,546-bp bands, and the 6,531-bp SacI band was cut into 2,941- and 3,675-bp bands. (C) Southern blot of viral DNAs derived from the wild-type virus (WT) and the ORF27− STOP mutant (27−), again with the BamHI-C genomic fragment as the probe template. With the STOP mutation, the 5,611-bp EcoRI band was cut into 4,075- and 1,536-bp bands. The predicted bands for ScaI digestion of the WT viral DNA were 28,780 and 5,721 bp. Insertion of the STOP oligonucleotide disrupted the ScaI site at genomic coordinate 45480 to give a single band of 34,501 bp.