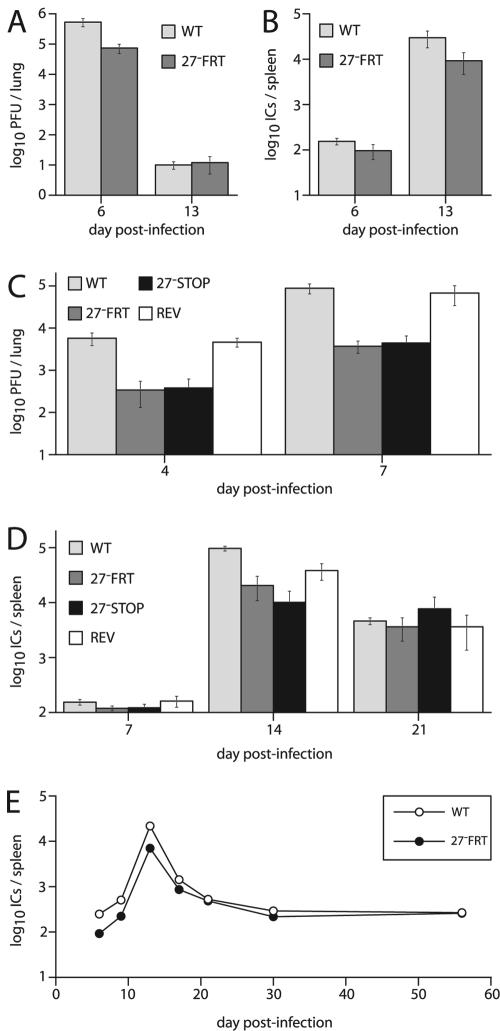
FIG. 6.
Growth of ORF27 mutant viruses in vivo. (A) BALB/c mice were infected intranasally (2 × 104 PFU/mouse) with the wild-type (WT) or ORF27-deficient (27− FRT) virus. Infectious viruses in the lungs were measured by a plaque assay. Means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) of five mice per group are shown. The reduction in titer with the ORF27− FRT virus on day 6 was significant by Student's t test (P < 0.03). (B) Latent viruses in the spleens of the same mice that were used for panel A were measured by an infectious center assay. Means ± SEM of five mice per group are shown. Although the 27− FRT titers were lower than those of the WT, the difference did not reach statistical significance in this experiment (P = 0.15). (C) C57BL/6J mice were infected intranasally (2 × 104 PFU/mouse) with ORF27+ (WT and REV) or ORF27− (STOP and FRT) viruses as indicated. Infectious viruses in lung homogenates were measured by a plaque assay at the indicated times. Means ± SEM of five mice per group are shown. Mutant virus titers were significantly lower than WT titers (P < 0.03), whereas the revertant titers (REV) were equivalent to WT titers (P = 0.7). (D) Latent viruses in the spleens of mice equivalent to those used for panel C were measured by an infectious center assay. Means ± SEM of five mice per group are shown. There was a significant reduction in the titers of the ORF27 mutants compared to the WT on day 14 after infection (P < 0.001) but not between the 27− FRT mutant and its revertant (REV). There was no significant difference between any of the groups at the other times. (E) BALB/c mice were infected intranasally (2 × 104 PFU/mouse) with the wild-type (WT) or ORF27-deficient (27− FRT) virus. Latent viruses in spleens were measured by an infectious center assay. Means ± SEM of five mice per group are shown, although the SEM error bars are smaller than the data points. The reduction in latent virus with the 27− FRT mutant was significant at days 6, 9, 13, and 17 postinfection (P < 0.03), but not at later times.