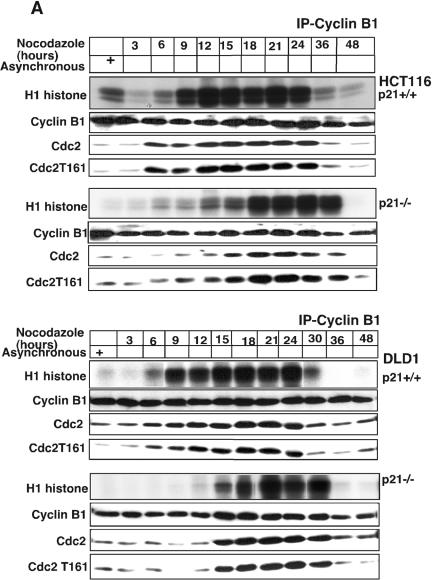
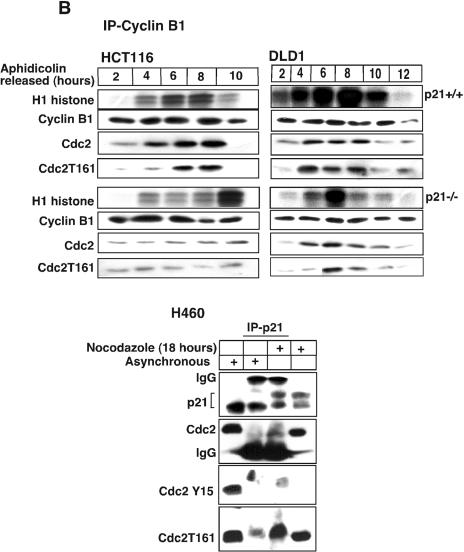
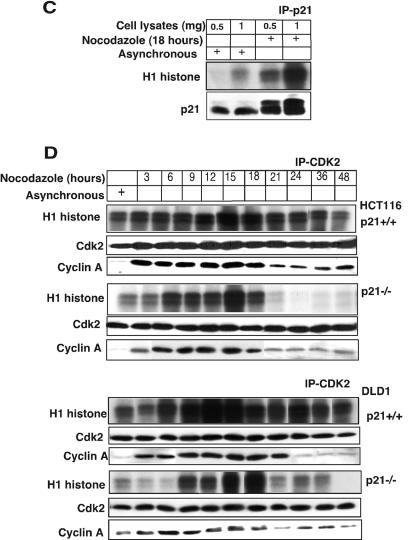
FIG. 4.
Absence of p21 in HCT116 and DLD1 cells delays cyclin B1-Cdc2 kinase activation. (A) Immnodepletion with cyclin B1 monoclonal antibodies in p21+/+ and p21−/− cell lysates collected after Nocodazole treatment at different time points was followed by an in vitro histone H1 kinase assay. The results demonstrate that the cyclin B1-associated kinase activity begins to rise at 6 h in HCT116 p21+/+ cells but is significantly delayed in p21−/− cells. In DLD1 p21+/+ cells, the H1 kinase activity also appears earlier than in p21−/− cells. Kinase activity was also observed to persist for 6 to 8 h longer following nocodazole exposure of HCT116 and DLD1 p21−/− cells than with the matched p21+/+ cells. Association between immunoprecipitated cyclin B1 and Cdc2 or T161-phosphorylated Cdc2 is shown. (B) Delayed histone H1 kinase activity was noted in aphidicolin-released cells immunodepleted with cyclin B1 antibody in p21−/− cells. Surprisingly, in DLD1 p21+/+ cells the kinase activity not only started at early time points but also progressed for longer time periods. However, the nocodazole exposure (A) or aphidicolin release (B) methods gave similar results with respect to the delay in cyclin B1-associated histone H1 kinase activation in the two different p21−/− human cell lines. Association between immunoprecipitated cyclin B1 and Cdc2- or T161-phosphorylated Cdc2 is shown. In the lower panels, association between p21- and T161-phosphorylated but not Y15-phosphorylated Cdc2 is shown. (C) Association of kinase activity with p21-containing immune complexes from cells enriched at G2/M. Nocodazole-treated G2/M-enriched H460 cells immunodepleted with p21 antibodies showed H1 histone phosphorylation. (D) CDK2-associated kinase activity is observed at all progressive time points following Nocodazole exposure with a peak at 15 to 18 h in p21+/+ cells (HCT116 and DLD1). After 18 h, the kinase activity returned to the basal levels in HCT116 and DLD1 p21−/− cells.