FIG.6.
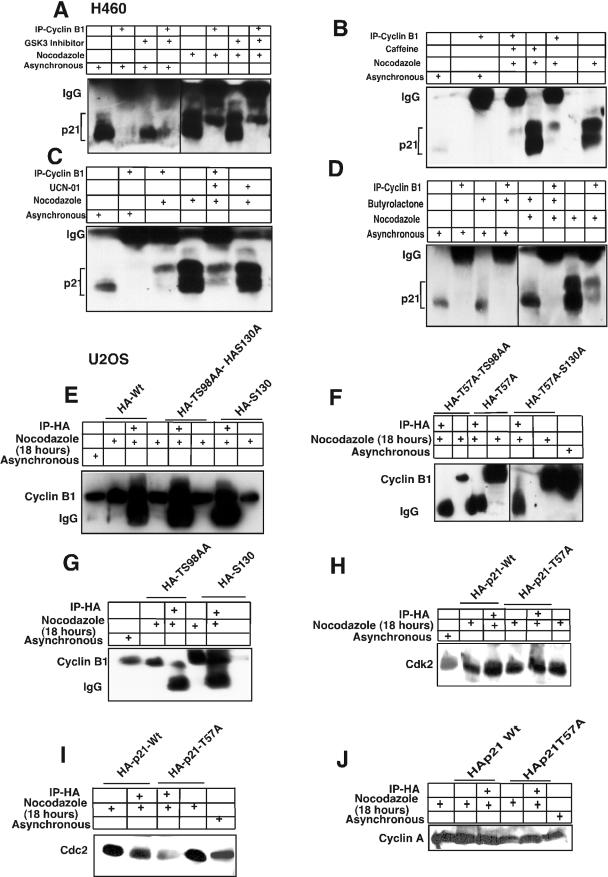
Cyclin B1 interacts specifically with phosphorylated Thr 57 of p21. (A) H460 cell lysates treated with nocodazole plus a GSK3 inhibitor (10 μM) and immunodepleted with anti-cyclin B1 antibody showed hyperphosphorylated p21 on the immunoblot. (B) Caffeine- plus nocodazole-treated cell lysates showed hyperphosphorylated p21 after immunodepletion with anti-cyclin B1 antibodies. Even though caffeine inhibits phosphorylation of p21 (Fig. 2D and F), residual hyperphosphorylated p21 immunoprecipitates with cyclin B1. (C) UCN-01, a PKC and Chk1 kinase inhibitor, did not prevent anti-cyclin B1 from immunoprecipitating the hyperphosphorylated p21 band in nocodazole-treated G2/M-arrested H460 cells. (D) Butyrolactone, the CDK inhibitor, blocked the interaction between cyclin B1 and p21 in G2/M-enriched nocodazole-treated cells. (E) Transient transfection of HA-tagged p21HA-Wt, p21HA-T98A, S99A mutant, or p21HA-S130A mutant in U20S cells for 24 h and treatment with nocodazole for 18 h did not prevent interaction between phosphorylated p21 and cyclin B1. (F) p21HA-T57A or p21HA-T57A,T98A, S99A mutant, or p21HAT57A,S130A did not immunodeplete cyclin B1 after immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibodies in nocodazole-treated cells. (G) Transfection of p21HA-T98A, S99A mutant, or p21HA-S130A and immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody showed in association with cyclin B1. (H) Transient transfection of p21HA-Wt or p21HA-T57A mutant constructs in U20S cells for 24 h and further treatment with nocodazole for 18 h followed by immunodepletion with anti-HA antibodies and immunoblotting with anti-CDK2 antibody showed CDK2 protein association. (I) p21HA-Wt or p21HA-T57A transient transfection in U20S cells treated with nocodazole for 18 h and immunodepleted with anti-HA antibody showed Cdc2 on the immunoblot. (J) p21HA-Wt or p21HA-T57A transfected in U20S cells and treatment with nocodazole for 18 h followed by immunodepletion with anti-HA antibodies and immunoblotted with cyclin A showed cyclin A association.