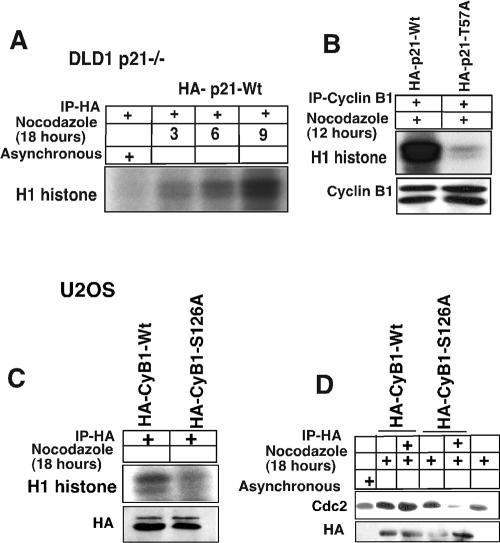
FIG. 8.
Kinase activity in DLD1 p21−/− cells after introduction of wild-type but not T57A-mutated p21 or in U2OS cells after introduction of wild-type but not S126A-mutated cyclin B1. (A) DLD1 p21−/− cells were transfected with a HA-tagged p21-Wt plasmid and treated with nocodazole for another 18 h. Histone H1 kinase assays were performed on the HA antibody-immunodepleted lysates, which showed H1 histone phosphorylation as early as after 3 h of nocodazole treatment. See panel B for an essential negative control. (B) p21HA-Wt or p21HA-T57A mutant plasmids were transfected in DLD1 p21−/− cells for 24 h, and the cells were treated with nocodazole for 12 h. Cell lysates were immunodepleted with anti-cyclin B1 antibodies, and H1 histone kinase assays were performed. The p21Wt construct-transfected DLD1 cells showed significantly higher phosphorylation of histone H1 compared to the T57A mutant. In nocodazole-treated DLD1−/− cells not transfected by a p21 expression plasmid, there was virtually no detectable cyclin B1-associated kinase activity (see Fig. 4A). (C) Plasmids expressing wild-type or S126A-mutated cyclin B1 tagged with HA were transfected into U2OS cells for 24 h, and the cells were treated with nocodazole for another 18 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody, and histone H1 kinase activity was determined. (D) U2OS cells were transfected with wild-type or S126A-mutated cyclin B1 tagged with HA for 24 h, and the cells were treated with nocodazole for another 18 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Cdc2 antibody.