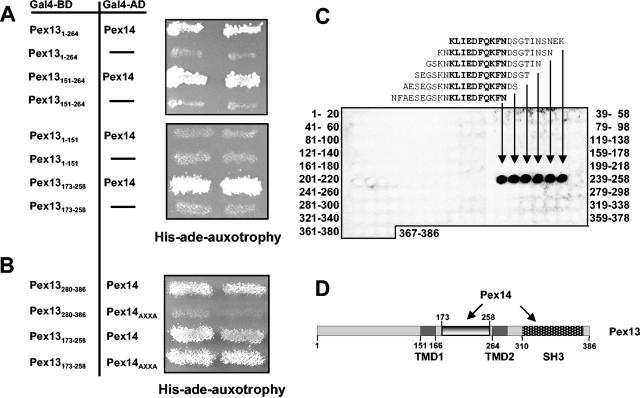
FIG. 1.
Identification of a novel Pex14-binding site in Pex13. (A) Interactions of Pex13 fragments with Pex14 in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Truncations of PEX13 were fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (Gal4-BD) and coexpressed with a PEX14-GAL4 activation domain (Gal4-AD) fusion in yeast strain PJ69-4A. As control, the bare Gal4-AD was coexpressed with the Pex13-Gal4-BD fusion. Two independent transformants were tested for prototrophy on plates lacking both histidine and adenine. The following plasmids were used to express the indicated Pex13 fragments: Pex131-151 (pKat31), Pex131-264 (pKat33), Pex13151-264 (pKat129), and Pex13173-258 (pKat145). (B) Involvement of the proline-rich motif of Pex14 in binding to Pex13. The two Pex14-interacting fragments of Pex13, comprising the SH3 domain (Pex13280-386) and the novel binding site (Pex13173-258), were tested for interactions with Pex14 mutated in its proline-rich motif (Pex14AXXA; pWG14/6) as described for panel A. (C) In vitro binding of Pex14 to the novel binding site of Pex13. Synthetic 20-mer peptides with two-amino-acid shifts between neighboring peptides and representing full-length Pex13 were synthesized on cellulose membranes. The identities of the first and the last peptides in each line of the peptide array are indicated. The membranes were incubated with purified recombinant GST-Pex14 followed by monoclonal anti-GST antibodies. Pex13 peptides that bound to GST-Pex14p were visualized with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse antibodies and ECL reagent. The sequences of the interacting peptides are shown, and the overlapping amino acids are highlighted by bold type. (D) Schematic view of Pex13 and, its proposed transmembrane domains TMD1 and TMD2, the SH3 domain, and the novel Pex14-binding site. Numbers denote amino acid positions.