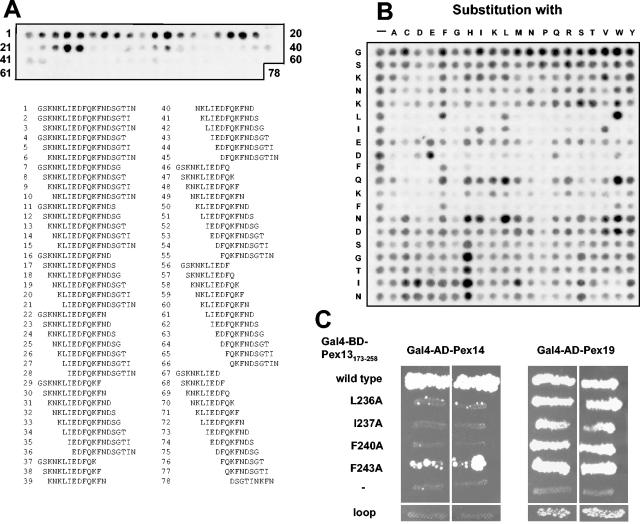
FIG. 2.
Characterization of the second Pex14-binding site in Pex13. (A) Length analysis of the novel Pex14-binding site. Peptides comprising systematic truncations of Pex14-interacting peptide Pex13231-250 down to a length of nine amino acids were synthesized on cellulose membranes and incubated with purified His6-Pex14. Bound His6-Pex14 was visualized immunologically with monoclonal anti-His6 antibodies. The numbered peptide sequences shown below the membrane correlate with the spot numbers on the membrane. (B) Substitution analysis. Pex14 was tested for interactions with mutated variants of Pex13231-250 peptide GSKNKLIEDFQKFNDSGTIN as described for panel A. The first row represents the nonmutated wild-type peptide, whereas peptides in all other rows harbor the indicated single amino acid substitutions. Spots with reduced intensities represent peptides with reduced binding affinities for Pex14. (C) In vivo effect of mutating critical residues of the Pex14-binding site. (Left panels) A yeast two-hybrid assay was used to study the interaction of Pex14 with Pex13173-258 that had been mutated to A at position L236 (pAS40), I237 (pAS41), F240 (pAS42), or F243 (pAS43) or at all four positions (loop; pAS82). (Right panels) As a control, the Pex13 fragments were also assayed for interactions with Pex19, which require amino acids 200 to 220 of Pex13. BD, DNA-binding domain; AD, activation domain.