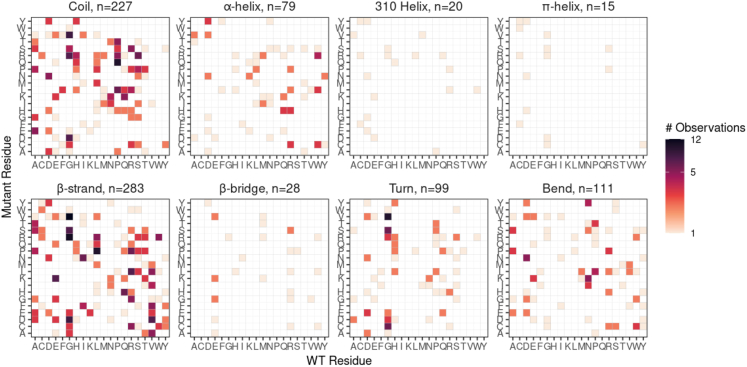
Figure 5.
The wild-type and mutant residues for each of the 862 unique amino acid changes observed in this study
Some of the specific substitutions are present in different proportions based on the type of secondary structure. Glycine (G) is the most commonly mutated wild-type residue (i.e., within columns); conversely, arginine (R) is the most common mutant residue observed (i.e., within rows), although this pattern is not as visually striking, because the majority are G > V.