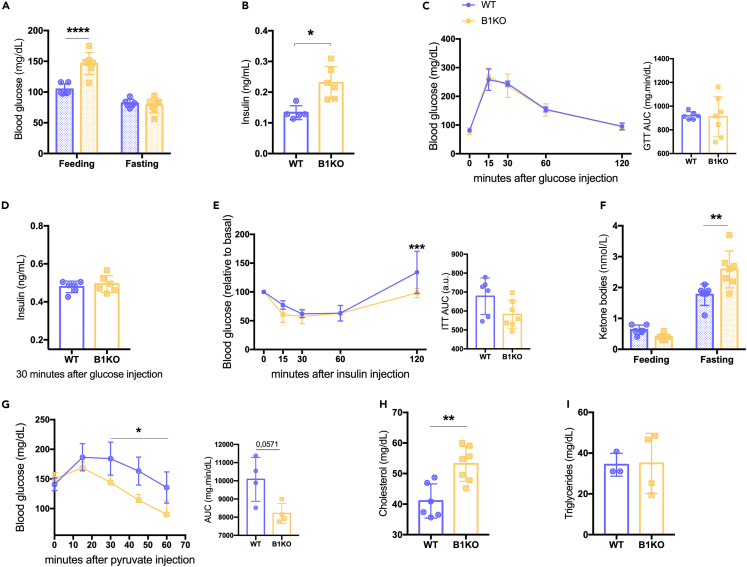
Figure 1.
The lack of B1R increased blood glucose and insulin levels in female mice
Effects of B1R deficiency on feeding and fasting glycemia (A); serum fasting insulin level (B); glucose tolerance test (C); serum insulin level 30 min after glucose injection test (D); insulin tolerance (E); feeding and fasting β-ketone levels (F); pyruvate tolerance test (G); and serum cholesterol (H) and triglycerides (I) levels. The lack of B1R increases feeding glycemia (p < 0.0001), fasting insulin (p = 0.004), β-ketone (p = 0.001), and cholesterol (p = 0.003) levels and reduces the pyruvate tolerance (genotype as the source of variation: p = 0.032). Interaction between genotype and feed state was found for glycemia (p = 0.0001) and ketone levels (p = 0.001); and between genotype and time for pyruvate tolerance test (p = 0.001). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data were compared by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test (A, C, D, F, and G), Mann-Whitney (B and I), and Student’s unpaired t test (D and H) at GraphPad Prism 7. Values expressed as mean ± SD of 3–7 mice per group. AUC – area under the curve. Lilac circle = virgin WT female; Yellow square = virgin B1KO female.