FIG. 5.
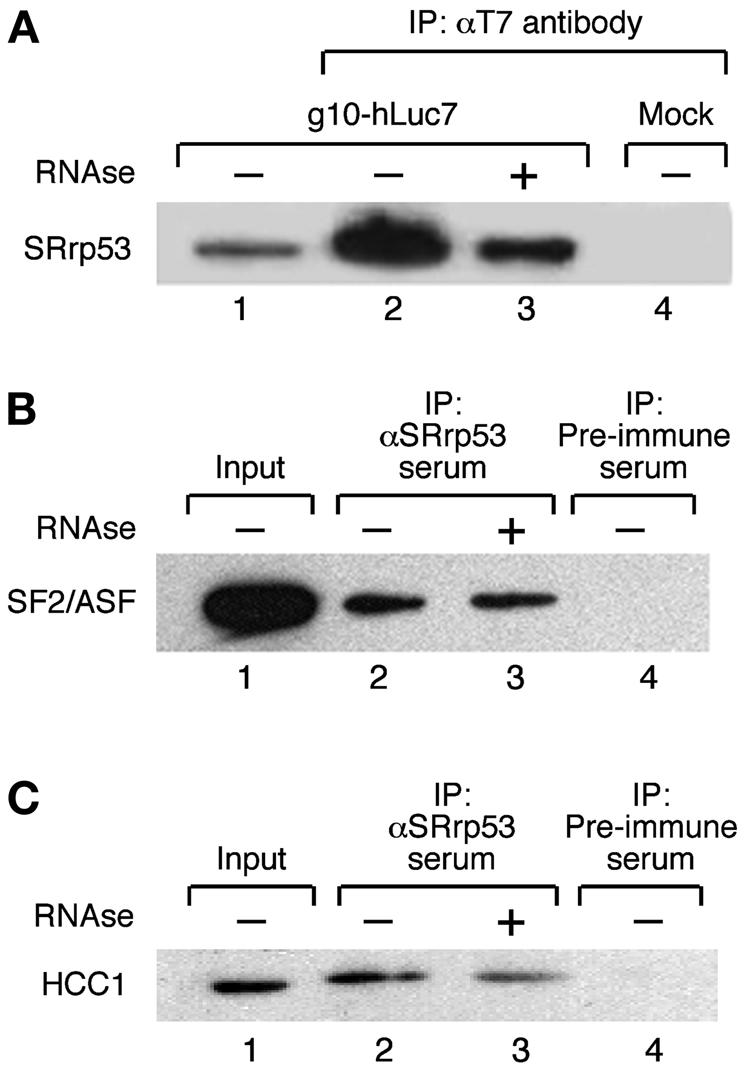
SRrp53 interacts with splicing factors in cultured mammalian cells. (A) IP assays with T7-hLuc7a are shown. Extracts prepared from 293T cells either transiently transfected with a plasmid encoding T7-hLuc7a (lanes 2 and 3) or mock transfected (lane 4) were incubated with anti-T7 antibody bound to Sepharose beads (Novagen). The bound proteins were separated on an SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-SRrp53B4 antibody. Alternatively, the immunoprecipitate was treated with RNase before loading on the gel (lane 3). Lane 1 was loaded with 2% of the amount of extract used for each IP. (B) Extracts prepared from 293T cells were incubated with either anti-SRrp53B4 antibody (lanes 2 and 3) or preimmune serum (lane 4) bound to Sepharose beads and analyzed as described for panel A. The blot was probed with MAb 96 antibody, which recognizes SF2/ASF (25). Alternatively, the immunoprecipitate was treated with RNase before loading on the gel (lane 3). Lane 1 was loaded with 2% of the amount of extract used for each IP. (C) The interaction between SRrp53 and HCC1 was analyzed as described for panel B. The blot was probed with a polyclonal antibody raised in sheep, which specifically recognizes HCC1.
