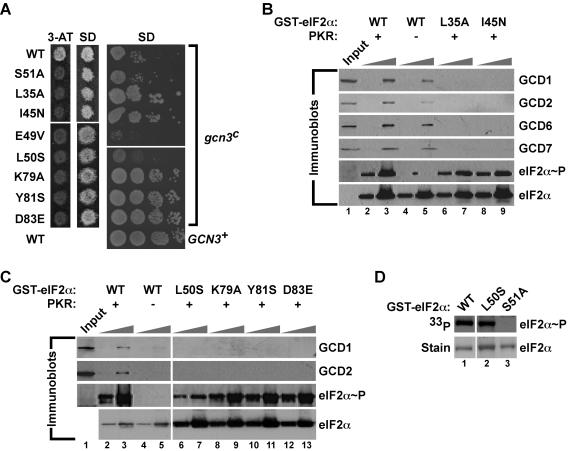
FIG. 7.
eIF2α mutations near and remote from Ser51 impair eIF2B binding to phosphorylated eIF2α. (A) Effects of selected eIF2α mutations on amino acid analog sensitivity and growth rate in yeast expressing WT GCN3 (left panels) or the gcn3c-R104K mutant (right panel). (Left panels) Transformants of yeast strain H1643 expressing the indicated eIF2α alleles were grown to confluence on an SD plate and replica plated to a 3-AT plate (30 mM) and an SD plate. Plates were incubated for 3 days at 30°C. (Right panel) Derivatives of yeast strain H1658 (MATα ura3-52 leu2-3 leu2-112 ino− trp1-Δ63 sui2Δ gcn3c-R104K p[SUI2, URA3] 〈HIS4-lacZ, ura3-52〉) expressing the indicated eIF2α mutants were generated by plasmid shuffling, and the resulting strains were tested for growth on SD medium by spotting 10-fold serial dilutions of a saturated culture and incubating for 3 days at 30°C. As a control, WT GCN3 on a low-copy-number plasmid (GCN3+) was introduced into the strain bearing WT eIF2α to complement the recessive gcn3c-R104K mutation. (B and C) Mutations of eIF2α residues near and remote from Ser51 impair binding of eIF2B subunits to phosphorylated eIF2α. WT GST-eIF2α and the indicated mutant derivatives were purified from bacteria and incubated with (+) or without (−) PKR in kinase buffer. Two different amounts of GST-eIF2α fusion proteins (0.1 and 1.0 μg) were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and then incubated with WCEs from yeast overexpressing all five eIF2B subunits. After extensive washing, bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against GCD1, GCD2, GCD6, GCD7, and Ser51-phosphorylated eIF2α, as indicated. The eIF2α blot was stripped and reprobed with polyclonal antisera against total yeast eIF2α. Input lanes contained 10% of the WCEs used in each reaction. (D) Efficient phosphorylation of eIF2α-L50S by PKR in vitro. The indicated WT and mutant GST-eIF2α fusion proteins were purified from bacteria and incubated with recombinant PKR and [γ-33P]ATP. Reaction mixtures were resolved by SDS-PAGE, proteins were detected by Coomassie staining (lower panels), and eIF2α phosphorylation was analyzed by autoradiography (upper panels).