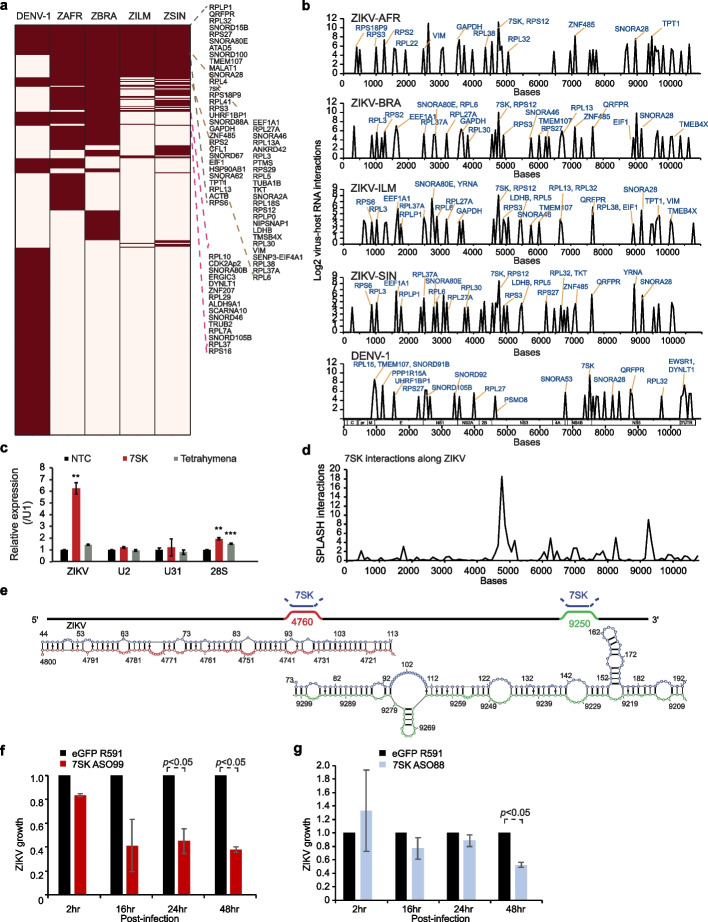
Fig. 4.
Noncoding RNAs interact with DENV and ZIKV genomes and impact virus fitness. a Heatmap showing the host RNAs that interact with DENV-1 and 4 strains of Zika. Host RNAs that interact with more than 3 viruses are listed on the right of the heatmap. b Locations of top 50 virus-host interaction sites along DENV-1 and the 4 ZIKV strains. Many of the top virus-host interaction sites are conserved across the viruses (shown in red). c qPCR analysis of ZIKV, U2, U31 and 28S rRNA pulled down by 7SK and tetrahymena RNA. Tetrahymena RNA is used as a negative control. **, *** indicate p-values ≤ 0.01 and 0.001 respectively, using Student’s T-test. d Locations along ZIKV that bind to 7SK RNA. The Y-axis indicates the number of SPLASH interactions between ZIKV and 7SK at that position. e Top, schematic of the strongest ZIKV-7SK interactions along the ZIKV genome. Bottom, predicted pairing interactions between ZIKV and 7SK using the program RNAcofold. 7SK sequences are shown in blue and the two ZIKV interaction sequences are in red and green respectively. f, g Bar charts showing the amount of ZIKV inside Huh7 cells at 2,16, 24, and 48 h post-infection, using qPCR analysis. ZIKV amount inside cells is decreased upon knockdown of 7SK using ASO99 (f) and after its interaction with 7SK is blocked using a 2’O-methylated anti-sense oligo to 7SK (ASO88) (g)