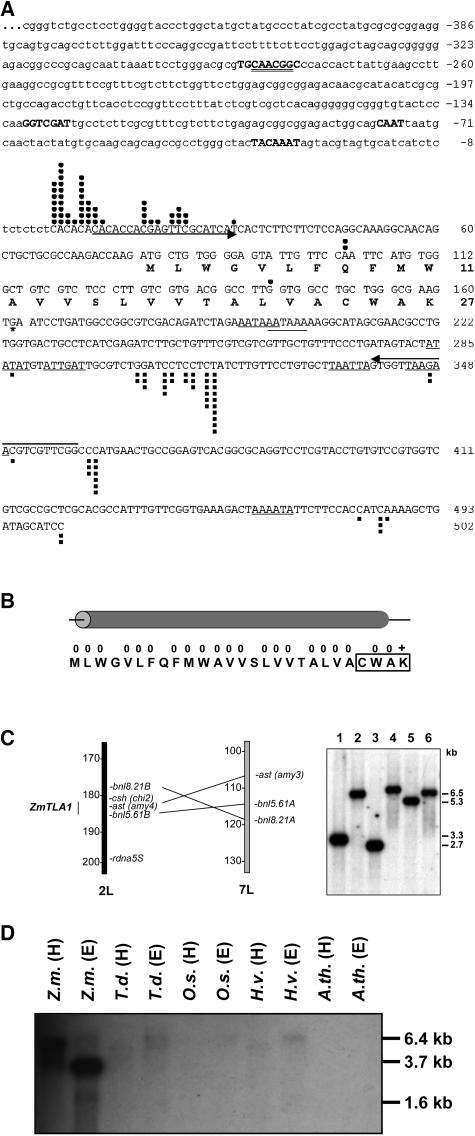
Figure 1.
The ZmTLA1 Gene Is Highly Expressed in Egg Cells and Encodes a Small Hydrophobic Peptide.
(A) A total of 52 ZmTLA1 cDNAs were isolated out of 988 egg cell ESTs and after differential screening of an egg cell cDNA library of maize. Black dots mark transcription start points of individual transcripts, and black squares indicate poly(A) sites. Seven putative poly(A) signal sites are underlined by a single line. The asterisk marks the putative stop codon. Upstream (869 bp) of the most frequently used transcription start points C and A at positions +1 and +2, respectively, were cloned as the ZmTLA1 promoter (445 bp of the promoter sequences are shown in lower-case letters). Putative TATA- (TACAAAT), CAAT- (gCAATt), an auxin responsive element (GGTCGAT), and an MSA-box (TGCAACGGC) are marked by bold capital letters within the ZmTLA1 promoter sequence, and a putative Myb Hv1 binding element is double underlined. Arrows mark primers sites that were used for single cell RT-PCR and genomic amplifications.
(B) The ZmTLA1 predicted peptide consists of 27 mainly hydrophobic amino acid residues (0) with one positively charged amino acid (+) at the very C terminus. The Caax-like motif is boxed, and the whole peptide is predicted to form an α-helix.
(C) The intronless ZmTLA1 gene maps to the long arm of chromosome 2 (2L) between the molecular markers csh (chi2) at position 181.2 and bnl5.61B at position 185.0. This region of chromosome 2 is known to be duplicated on chromosome 7 (left). Despite this duplication, ZmTLA1 represents a single copy gene as indicated by the genomic DNA gel blot hybridization (right). Genomic DNA of the maize inbred line A188 was separated in a 0.7% agarose gel after digestion with the following restriction enzymes: XhoI (1), HindIII (2), EcoRI (3), EcoRV (4), DraI (5), and NdeI (6). Exposure at −70°C was performed for 3 d using intensifier screens.
(D) Orthologous TLA1 genes were detected in maize (Z.m.), Tripsacum dactyloides (T.d.), rice (O.s.), and barley (H.v.) but not in Arabidopsis (A.th). Genomic DNA was restricted with HindIII (H) and EcoRI (E), separated in a 1.2% agarose gel, blotted, hybridized, and washed at high stringency conditions. Exposure at −70°C was performed for 14 d using intensifier screens.