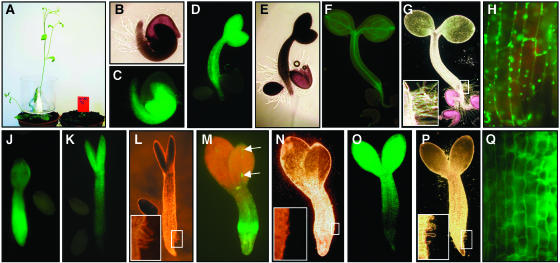
Figure 7.
Ectopic Expression of ZmTLA1 in Arabidopsis Suppressed Developmental Processes, Including Cell Morphogenesis.
(A) Wild-type (ecotype Wassilewskija) and kanamycin-selected transgenic Arabidopsis plants 32 dag.
(B) to (H) Germination of Arabidopsis seedlings containing a cytoplasmic GFP (p35S:mGFP5-ER) as a control.
(B) and (C) Light- and UV-microscopic images of a seedling shortly after germination initiation showed morphogenesis of root hairs.
(D) and (E) UV- and light-microscopic images of a seedling 3 dag showed root elongation.
(F) and (G) UV- and light-microscopic images of a seedling 5 dag showed further elongation of primary root and hypocotyl, greening, and, thus, biogenesis of chloroplast in the upper part of the hypocotyl and cotyledons. Inset in (G) shows an enlargement of the root hair zone.
(H) Enlargement of a hypocotyl region showed large cells with GFP signals in Golgi and Golgi-derived vesicles but not in the cell wall. Note the red fluorescence from mature chloroplasts.
(J) to (Q) Arabidopsis seedlings of different transgenic lines expressing an inducible ZmTLA1-GFP fusion protein. Development of seedlings was arrested at 6 to 10 dag in induction medium.
(J) UV microscopy of a seedling displaying strong GFP signals in the hypocotyl and root apex. Elongation of the hypocotyl and differentiation of root hairs and primary root were suppressed.
(K) and (L) UV and light microscopy of a seedling displaying strong GFP signals in the upper part of the hypocotyl and cotyledons. Inset in (L) shows an arrest of root hair development. Note that cotyledons displaying strong GFP signals remained small.
(M) and (N) UV and light microscopy of a seedling displaying strong GFP signals only in the lower part of the hypocotyl. Arrows point toward GFP expressing cells in one cotyledon, which remained smaller than the second cotyledon. Inset in (N) shows the lack of root hair differentiation in the zone displaying strong GFP signals.
(O) and (P) UV and light microscopy of a seedling displaying strong GFP signals only in the upper part of the hypocotyl and cotyledons. Inset in (P) shows an arrest of root hair development.
(Q) Enlargement of a hypocotyl region of (O) showing less elongated hypocotyl cells with GFP signals exclusively in the cell wall.