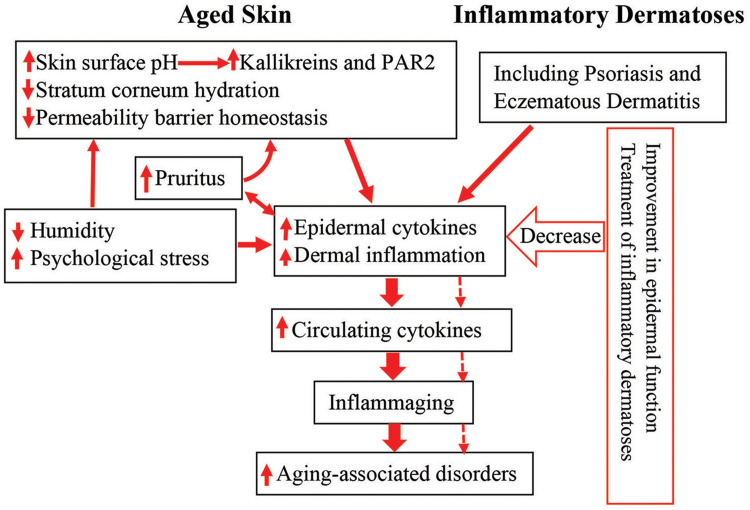
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram: link between cutaneous conditions and aging-associated disorders in the elderly. Aged humans exhibit epidermal dysfunction. Both epidermal dysfunction and inflammatory dermatoses can provoke cutaneous inflammation. Prolonged cutaneous inflammation can result in inflammaging, leading to the development of inflammaging-associated disorders in the elderly (indicated in solid arrows). Conversely, either appropriate treatment of inflammatory dermatoses or improvement in epidermal function can decrease cutaneous inflammation, preventing the development and progression of inflammaging, consequently alleviating inflammaging-associated disorders in the elderly (indicated in dotted arrows).
Abbreviation: PAR2, protease-activated receptor 2.