Fig. 1.
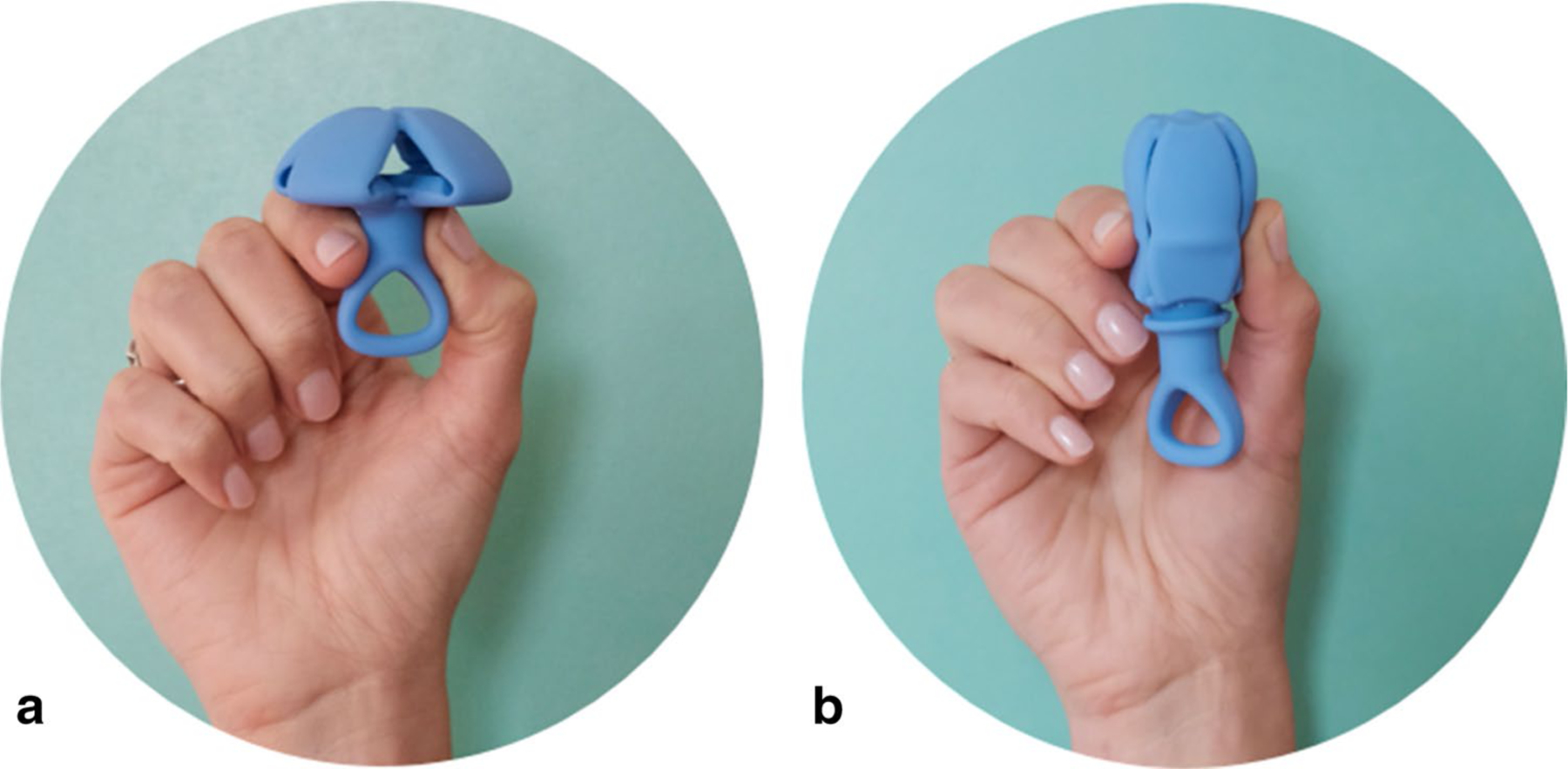
Study pessary. a Natural resting state when providing support. Once inserted, abdominal forces from above keep the pessary in position, similar to a Gellhorn pessary. b Temporary collapsed state during insertion and removal (with 50% reduction in cross-sectional diameter compared to resting state). Collapsed state is achieved with traction on the loop of the stem. Description of SP use: for insertion, the pessary is held in the “collapsed” state with one hand. Once inserted beyond the vestibule, the pessary is released and deploys into the “resting” state for prolapse support, with the stem oriented distally in the vagina. After deployment, abdominal forces maintains the pessary’s “resting” state and prevent expulsion. For removal, the pessary is pulled by a loop on its distal end, causing elongation as it is withdrawn from the vagina
