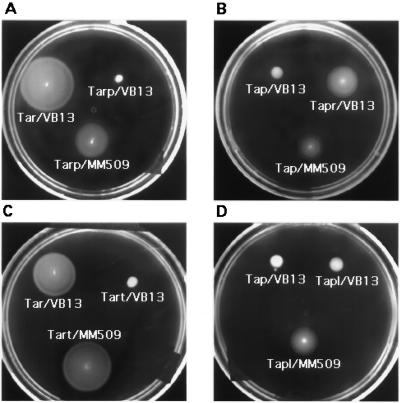
FIG. 2.
Chemotactic responses mediated by wild-type and hybrid receptors. Swarms were formed by colonies of strain VB13 (ΔT) or strain MM509 (Δtar-tap) carrying plasmids containing genes encoding the wild-type or hybrid receptors. (A and C) Aspartate swarm plates. (B and D) Pro-Leu swarm plates. Large, rapidly forming swarms with thick outer rings are characteristic of wild-type aspartate taxis, whereas more slowly developing, thin, sharp rings on the surface of the agar are characteristic of wild-type dipeptide taxis.