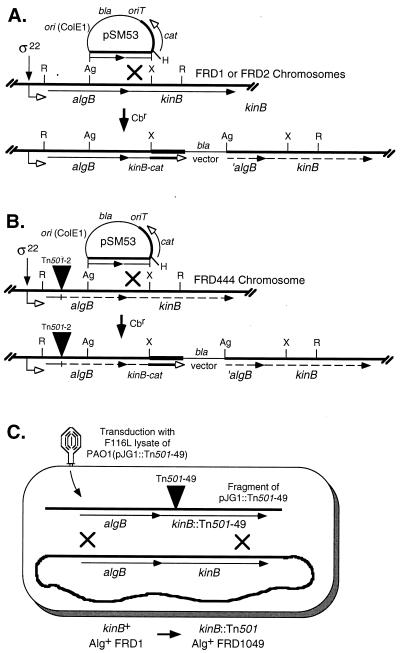
FIG. 1.
Diagram of genetic constructions used to modify the chromosomal kinB gene in P. aeruginosa FRD. (A) Construction of kinB-cat transcriptional fusion in Alg+ strain FRD1 and Alg− strain FRD2. A promoterless cat gene cassette (0.8-kb HindIII fragment) was cloned to form a kinB-cat transcriptional fusion in pSM53. This plasmid has a ColE1 origin, which cannot replicate autonomously in P. aeruginosa, and was integrated into the chromosomes of FRD1 and FRD2 (algT18) by homologous recombination via selection for carbenicillin resistance encoded by bla. Dashed arrows indicate genes that are not transcribed due to the polar upstream insertion of the vector. (B) Construction of kinB-cat transcriptional fusion in Alg− strain FRD444 (algB::Tn501-2). The Tn501 insertion in algB (closed triangle) is polar on downstream genes, as indicated by dashed arrows. (C) Construction of the kinB mutant FRD1049. A gene replacement technique (42) was used to transfer an kinB::Tn501 allele into the chromosome of P. aeruginosa FRD1. Briefly, a lysate of phage F116L was generated on P. aeruginosa PAO1(pJG1::Tn501-49) and used to transduce FRD1. Mercury resistance encoded by Tn501 was used to select for double-crossover events of kinB::Tn501 with the chromosome, and the strain was scored for loss of plasmid-borne tetracycline resistance. Abbreviations: Ag, AgeI; R, EcoRI; H, HindIII; X, XhoI; bla, gene encoding carbenicillin resistance; cat, gene encoding CAT.