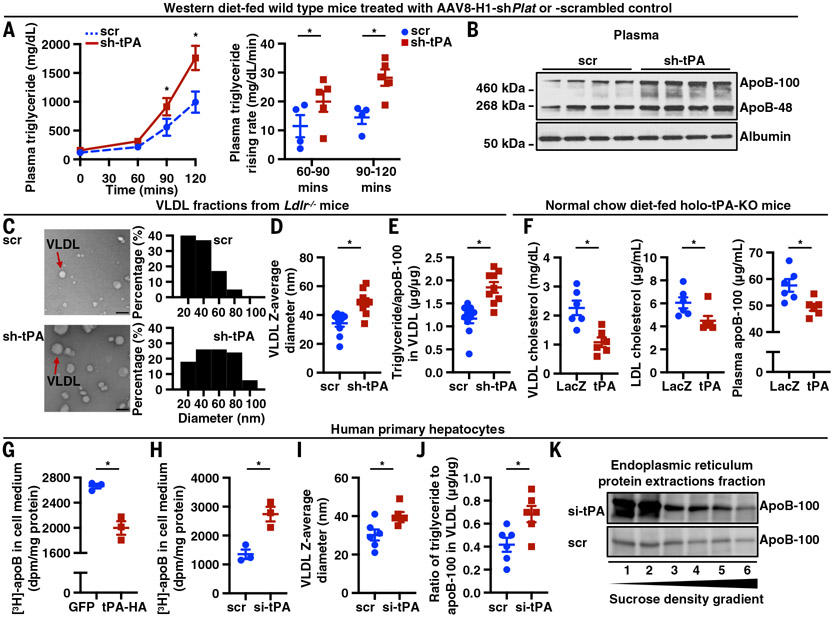
Fig. 2. tPA limits apoB lipidation in the ER.
(A) WT mice were treated with AAV8-H1-shPlat (sh-tPA) or AAV8-H1-scrambled control (scr) and then fed the WD for 14 weeks. Mice were injected with P407 intraperitoneally (i.p.) to assess VLDL secretion. Plasma triglyceride concentration was measured (n = 4 to 5 mice per group). (B) WT mice were treated with AAV8-H1-shPlat (sh-tPA) or AAV8-H1-scrambled control (scr) and then fed the WD for 14 weeks. Mice were injected with P407 i.p. to assess VLDL secretion. Plasma apoB concentration was measured by ELISA (n = 4 to 5 mice per group). (C) Ldlr−/− mice were treated with AAV8-H1-shPlat (sh-tPA) or AAV8-H1-scrambled control (scr) and then fed the WD for 8 weeks. VLDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation and visualized by transmission electron microscopy. VLDL (n = 100 for each group) diameter was measured and analyzed using Image-Pro Plus 10.0. Scale bars, 100 nm. (D) Ldlr−/− mice were treated with AAV8-H1-shPlat (sh-tPA) or AAV8-H1-scrambled control (scr) and then fed the WD for 8 weeks (n = 9 to 10 mice per group). VLDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation, and VLDL diameter was measured by dynamic light scattering. (E) Ldlr−/− mice were treated with AAV8-H1-shPlat (sh-tPA) or AAV8-H1-scrambled control (scr) and then fed the WD for 8 weeks. VLDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation and assayed for the ratio of triglyceride to apoB-100 (n = 9 to 10 mice per group). (F) Whole-body tPA knockout mice (holo-tPA-KO) were treated with AAV8-TBG-Plat (tPA) or AAV8-TBG-lacZ (LacZ) and then fed a normal chow diet for 8 weeks. Plasma samples were assayed for VLDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and apoB-100 concentrations (n = 6 mice per group). (G) Human primary hepatocytes were transduced with a plasmid encoding tPA with C-terminal HA tag (tPA-HA) or GFP. After 48 hours, apoB secretion was measured using a [3H]-labeling method as follows: hepatocytes were incubated for 20 min in [3H]-leucine–containing medium and chased for 3 hours in [3H]-leucine–free medium, and then radioactivity associated with apoB in the cell medium was quantified by scintillation counting. (H) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with siRNA against tPA mRNA (si-tPA) or scrambled RNA for 24 hours. apoB secretion was measured using [3H]-labeling, as in (G). Radioactivity associated with apoB in cell medium was quantified by scintillation counting. (I) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with siRNA against tPA mRNA (si-tPA) or scrambled RNA for 24 hours. VLDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation, and VLDL diameter was measured by dynamic light scattering. (J) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with siRNA against tPA mRNA (si-tPA) or scrambled RNA for 24 hours. VLDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation and assayed for the ratio of triglyceride to apoB-100. (K) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with siRNA against tPA mRNA (si-tPA) or scrambled RNA for 24 hours. The ER fraction was isolated, and proteins from the ER were extracted. apoB-lipoproteins extracted from the ER were further separated by density gradient ultracentrifugation and divided into six fractions of increasing density from fraction 1 to 6. apoB from each fraction was measured by immunoblot. Data are shown as means ± SEMs; *P < 0.05 by two-tailed Student’s t test.