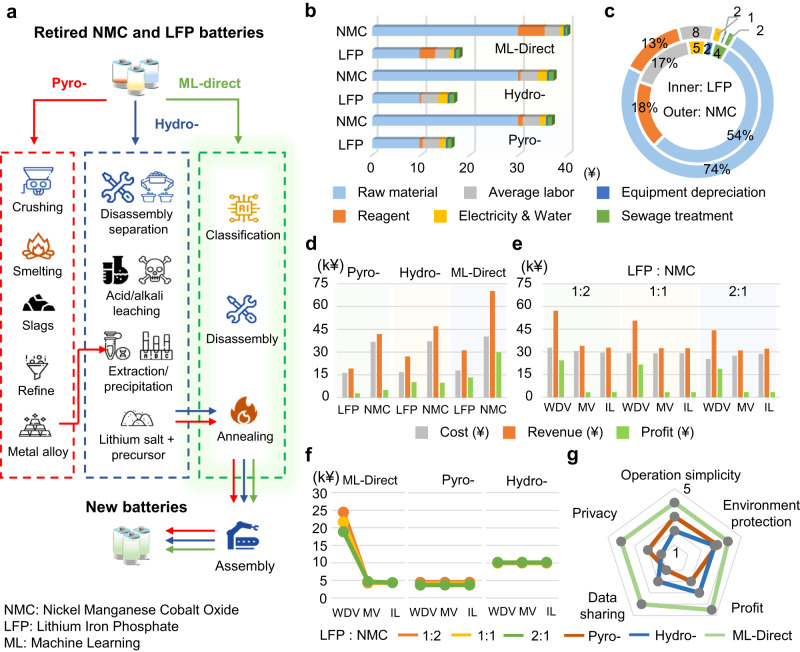
Fig. 5. An economic evaluation of retired battery recycling.
a Comparison of the Pyro- (pyrometallurgical), Hydro-(hydrometallurgical), and ML-direct (machine learning aided direct) recycling methods. b Cost analysis of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC) batteries using different recycling methods in individual modes. c Cost analysis of LFP and NMC batteries using ML-direct recycling in individual mode. d Cost, revenue, and profit comparison of the individual battery type using different recycling methods in individual mode. e Cost, revenue, and profit comparison using Wasserstein distance voting (WDV), majority voting (MV), and independent learning (IL) methods in hybrid mode. The ratio is the amount of LFP battery to that of NMC battery. f Sensitivity analysis of the profit of WDV, MV, and IL methods in a hybrid model towards sorting accuracy in hybrid mode. The ratio is the amount of LFP to that of the NMC battery. g Comprehensive comparison of different battery recycling technologies in hybrid mode. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The graphics in panel a were created using icons from Flaticon.com.