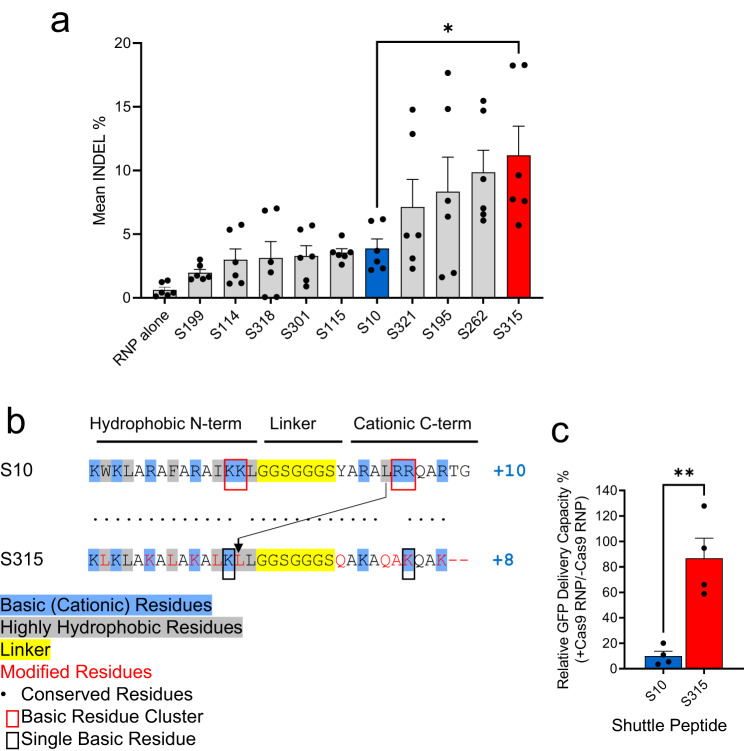
Fig. 1. Identification of shuttle peptides with improved delivery of Cas9 RNPs to airway epithelia.
a Delivery of Cas9 RNP (ribonucleoprotein) targeting CFTR locus in human airway epithelial cells cultured at the air liquid interface using indicated shuttle peptide candidates. Y axis represents the frequency of indels (insertions, deletions, and substitutions in the quantification window) attained with the indicated peptide. Individual closed circles represent data from n = 6 independent samples. Blue and red color represent the peptides used further in the study (S10 and S315, respectively). Results plotted as mean + SEM. Statistics by unpaired two-tailed t test, *P = 0.01. b Comparison of the amino acid sequences of S10 and S315 peptides. c Inhibitory effect of Cas9 RNP on S10- or S315-mediated delivery of GFP to CFF-16HBEge cells. GFP (green fluorescent protein, 10 μM), S10 or S315 (10 μM) peptide with or without Cas9 RNP (containing 2.5 μM Cas9 and 2 μM gRNA) were added to cells and GFP delivery quantified by flow cytometry. The Y axis represents the relative delivery activity (%), calculated as the GFP delivery attained with or without Cas9 RNP addition. Results plotted as mean + SEM. Statistics by unpaired two-tailed t test, **P = 0.003. Individual circles represent average data from n = 20,000 cells examined over 4 independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data File.