Figure 2. Molecular mechanisms of acute kidney disease.
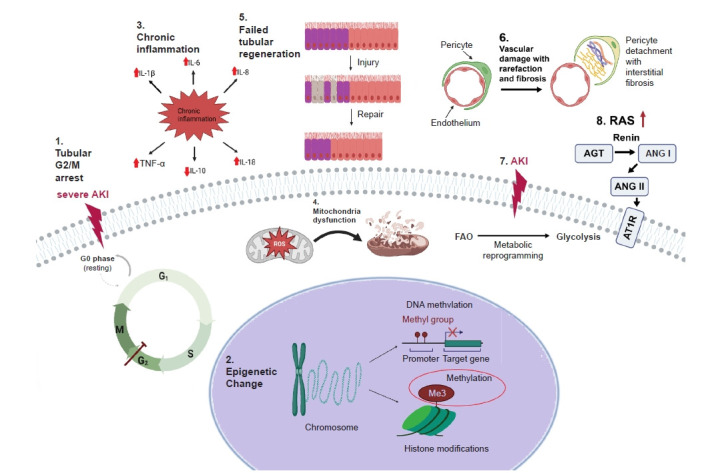
(1) Renal tubular epithelium cell-cycle arrest, (2) epigenetic change, (3) chronic inflammation, (4) dysfunction of mitochondria, (5) failed regeneration of tubular cells, (6) endothelial dysfunction, (7) metabolic reprogramming, and (8) RAS activation.
AGT, angiotensinogen; AKI, acute kidney disease; ANG I, angiotensin I; ANG II, angiotensin II; AT1R, angiotensin type-1 receptor; FAO, fatty acid β-oxidation; IL, interleukin; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α.
