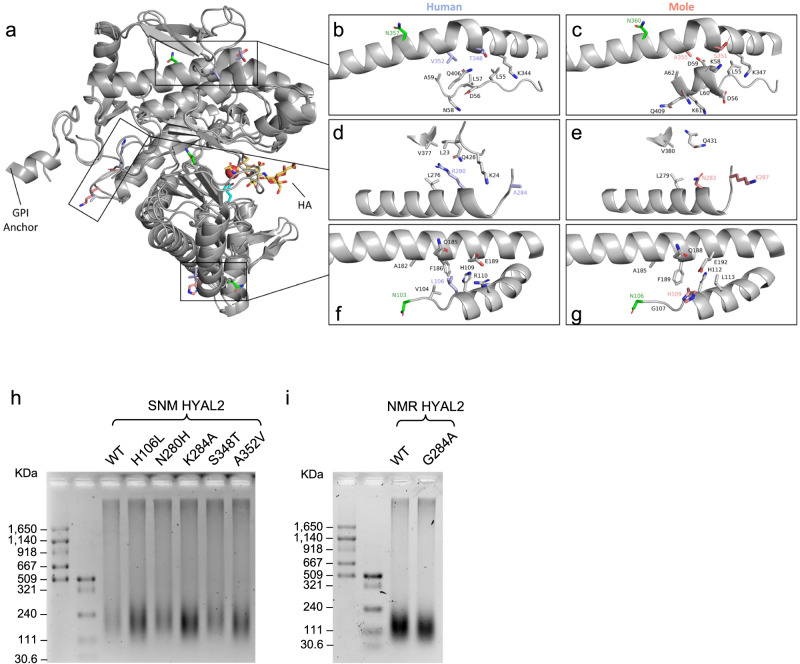
Fig. 5. Structural and functional analysis of EM and SNM HYAL2 mutations.
a Cartoon representation of human HYAL2 ranging from residues 21 to 448 as predicted by AlphaFold. For the positively selected sites identified in moles, the corresponding human residues are shown in orange and mole residues are shown in purple. Catalytic residues are shown in cyan and glycosylated residues in green. A molecule of HA tetramer (yellow) from bee venom HYAL (PDB code: 1FCV) was mapped to human HYAL2 using the PyMOL align function. b, c Zoomed in image of mutant residues 348 and 352 comparing human and moles. d, e Zoomed in image of residues 280 and 284 comparing human and moles. f, g Zoomed in image of residue 106 comparing human and moles. Only neighboring residues to the amino acids under positive selection in moles are shown. h, i Effect of SNM and NMR HYAL2 mutations on HA degradation. h HeLa cells were transfected with either wild-type (WT) SNM HYAL2 plasmid, or each of its five mutants. i HeLa cells were transfected with either NMR HYAL2 WT or the G284A mutant. Cells were incubated with media containing 10 μg/mL commercial HA for three days, followed by HA extraction an electrophoresis. h, i experiments were performed three times with similar results.