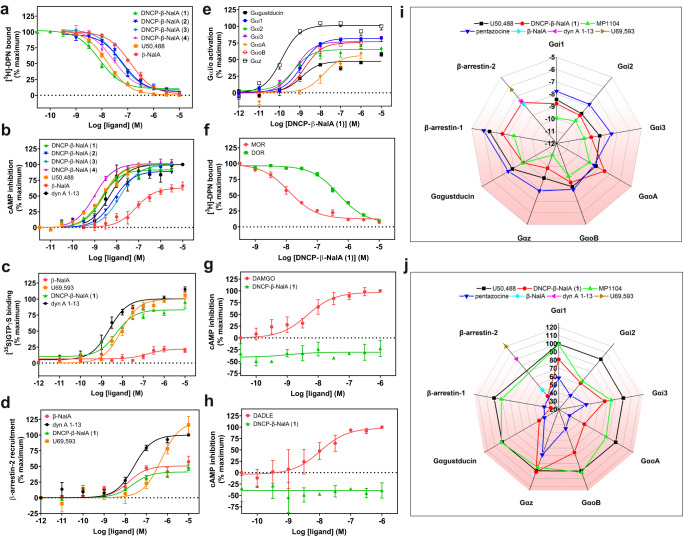
Fig. 3. In vitro receptor pharmacology of peptide–small molecule conjugates.
a, b Radioligand binding (n = 3) and functional cAMP assays (n = 3–4) of DNCP-β-NalA conjugates (1–4) were performed on HEK293T cell membranes stably expressing mouse KOR. Binding (a) was measured by displacing 1 nM of [3H]DPN whereas cAMP inhibition (b) was monitored after treatment with indicated concentrations of conjugates. U50,488 and β-NalA were positive controls. Final concentration of 10 µM of forskolin was used to stimulate cAMP production (Supplementary Table 3). c Concentration-dependent stimulation of [35S]GTPγS binding by the most potent DNCP-β-NalA(1) (n = 3), β-NalA (n = 3), U69,593 (n = 3) and dyn A1-13 (n = 4) in human KOR expressing CHO cell membranes (Supplementary Table 4). d β-arrestin-2 recruitment assay of DNCP-β-NalA(1), β-NalA and dynorphin (dyn) A1-13 was done in HEK293T cells transiently expressing mouse KOR-EGFP and β-arrestin-2-nano-luciferase (n = 3–6) (Supplementary Table 3). e α-Subtype screening of DNCP-β-NalA(1) at the mouse KOR in the TRUPATH assay (n = 8) (Supplementary Tables 5 and 6). f Selectivity of DNCP-β-NalA(1) was determined in a radioligand binding assay using HEK293T cell membrane preparations stably expressing mouse MOR and DOR and 1 nM of [3H]DPN, respectively (n = 3). g, h Gαi-mediated cAMP inhibition of DNCP-β-NalA(1) at the mouse MOR (g) and DOR (h) was measured in stable HEK293T cells using DAMGO and DADLE as reference ligands, respectively (n = 3). i, j Spider plots from TRUPATH (n = 8 for each Gα), β-arrestin-1 (n = 4) and β-arrestin-2 (n = 3–6) recruitment assays represent potency (log EC50) (i) and normalized efficacy (j) of DNCP-β-NalA(1), U50,488, MP1104, pentazocine, β-NalA and dyn A1-13. Data were normalized to full KOR agonists U50,488, U69,593 or dyn A1-13, full MOR agonist DAMGO and full DOR agonist DADLE. All data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.