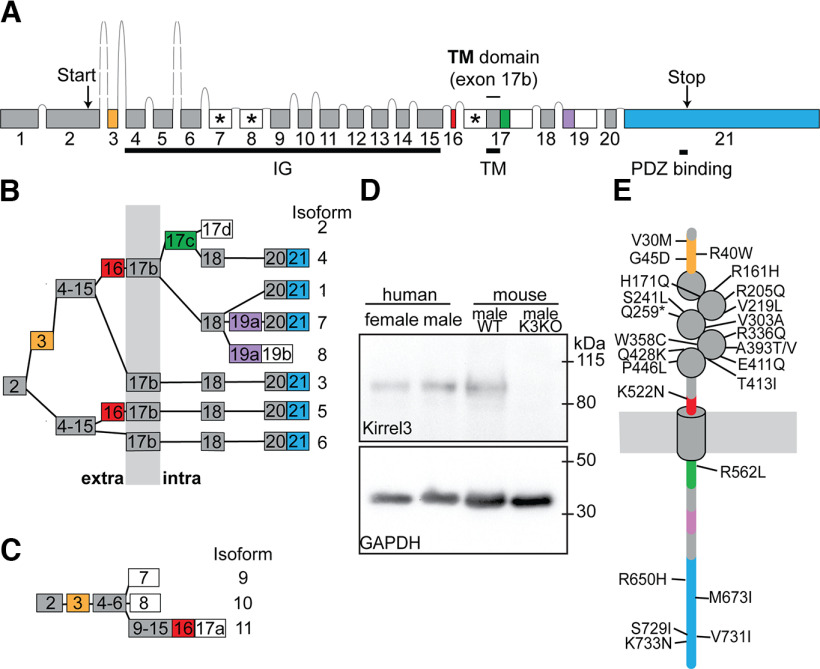
Figure 5.
Human Kirrel3 gene, transcript isoforms, and proteins. A, Genomic organization of the human Kirrel3 gene, with exons (boxes) and introns (lines), including five independently spliced protein-coding exons (yellow, red, green, purple, and blue). White boxes mark exons or exon parts with a stop-codon. Exons producing predicted secreted Kirrel3 isoforms are additionally marked with an asterisk. B, Alternative splicing of Kirrel3 exons is predicted to produce eight different transmembrane isoforms. Isoforms are given numbers, following the example of previously identified isoforms 1–3. White boxes indicate exons or exon parts with stop-codon. Exons encode protein segments that are either extracellular (“extra”), intracellular (“intra”), or spanning the membrane (gray vertical bar). C, Three predicted secreted Kirrel3 isoforms (9–11) only comprise extracellular domains. D, Western blot showing that Kirrel3 protein containing human exon 21 is found in brain lysates prepared from male and female postmortem tissue (see methods). Mouse wildtype (WT) and knockout (KO) lysates are used as a positive and negative control. E, Schematic of Kirrel3 proteins with the position of protein domains relative to the membrane (horizontal gray bar) and mutations associated with autism. IG: Ig-domain, TM: transmembrane domain.