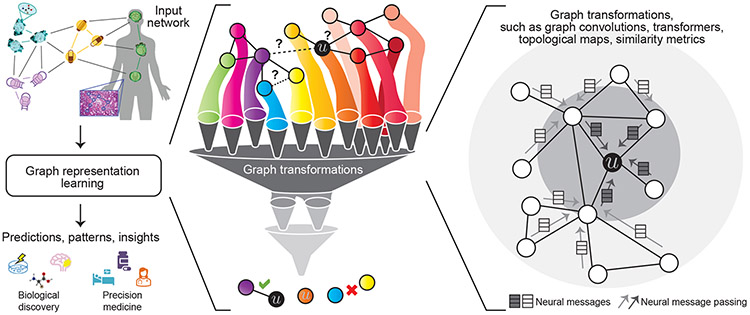
Figure 1: Representation learning for networks in biology and medicine.
Given a biomedical network, a representation learning method transforms the graph to extract patterns and leverage them to produce compact vector representations that can be optimized for the downstream task. The far right panel shows a local 2-hop neighborhood around node , illustrating how information (e.g., neural messages) can be propagated along edges in the neighborhood, transformed, and finally aggregated at node to arrive at the ’s embedding.