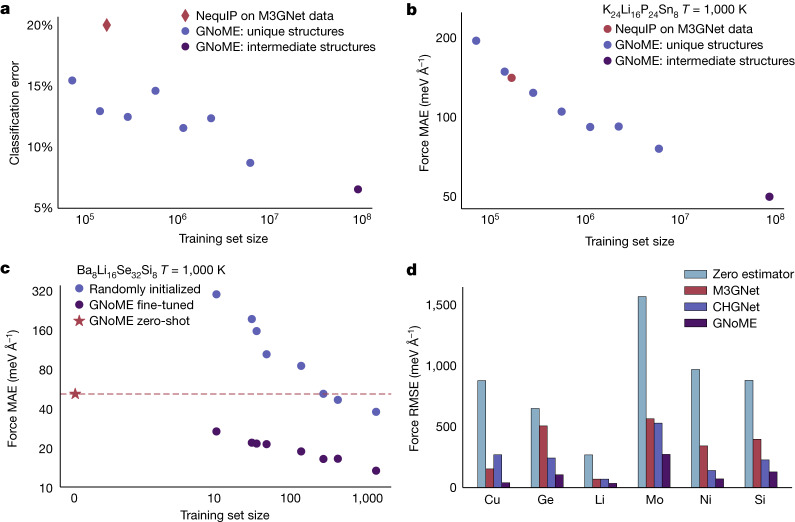
Fig. 3. Scaling learned interatomic potentials.
a, Classification of whether a material is a superionic conductor as predicted by GNoME-driven simulations in comparison with AIMD, tested on 623 unseen compositions. The classification error improves as a power law with training set size. b, Zero-shot force error as a function of training set size for the unseen material K24Li16P24Sn8. c, Robustness under distribution shift, showing the MAE in forces on the example material Ba8Li16Se32Si8. A GNoME-pretrained and a randomly initialized potential are trained on data of various sizes sampled at T = 400 K and evaluated on data sampled at T = 1,000 K. The zero-shot GNoME potential outperforms state-of-the-art models trained from scratch on hundreds of structures. d, Comparison of zero-shot force errors of three different pretrained, general-purpose potentials for bulk systems on the test set of ref. 56. Note that the composition Ni is not present in the GNoME pretraining data. RMSE, root-mean-square error.