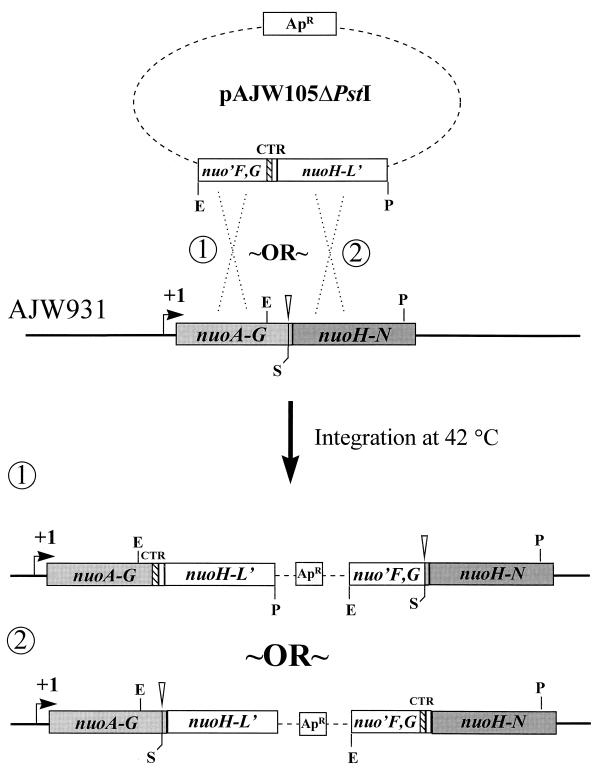
FIG. 3.
Construction of strain AJW1459 by integrational, homologous recombination. White bars, vector-derived nuo sequence; gray bars, chromosome-derived nuo sequence; dotted lines, vector sequence; ApR, ampicillin resistance. Other designations are as described in the Fig. 2 legend. The plasmid pAJW105ΔPstI encompasses the 3′ end of nuoF to the 3′ end of nuoL and carries the wild-type nuoG allele. This plasmid was transformed into competent AJW931 [ΔnuoG1 polA(Ts)] cells. Cells in which the plasmid had integrated into the chromosome by homologous recombination were identified by selection of ampicillin resistance at the restrictive temperature, 42°C. Strain AJW932 was constructed similarly (not shown), except that the plasmid pHF17, which carries the ΔnuoG1 allele, was integrated into the Nuo+ PolA(Ts) strain CP366. Similarly, strain AJW1472 was constructed by integrating pAJW105ΔPstI into strain AJW1470 [nuoG2 polA(Ts)]. The simultaneous presence of both the wild-type and mutant nuoG alleles in each of these strains was verified by PCR analysis with primers G1 and H1.