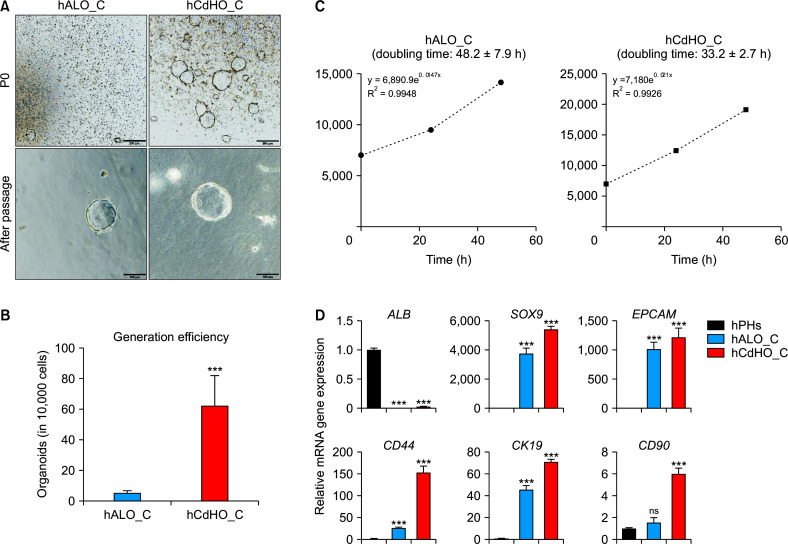
Fig. 2.
Characterization of hALO_C and hCdHO_C. (A) Bright-field images showing the generation of organoids of different origin hPHs or hCdHs at the generation stage (P0) and after sub-culture (after passage). Scale bar: 500 μm (top) or 100 μm (bottom). (B) Number of cells in hCdHO_C and hALO_C. Both hPHs or hCdHs were seeded into a 24-well cell culture plate with collagen solution. The number of cells in each organoid (hCdHO_C and hALO_C) was counted using a Nikon Eclipse Ti-e microscope. Data were obtained from triplicate experiments for a donor, hALO_C (n = 12) and hCdHO_C (n = 12). (C) Doubling time of hCdHO_C and hALO_C. Organoids were dissociated into single cells and cells were counted to analyze the doubling time for 48 h. (D) RT-qPCR of the hepatic marker (ALB) and hepatic progenitor markers (SOX9, EPCAM, CD44, CK19, and CD90) in hPHs, hALO_C, and hCdHO_C. Data on the expression of each gene marker were normalized against GAPDH. Data were analyzed by a two-tailed t-test. They are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of three individual experiments performed in triplicate. hPHs, human primary hepatocytes; hALO_C, hPH-derived organoids with collagen scaffold; hCdHs, human chemically derived hepatic progenitors; hCdHO_C, hCdH-derived organoids in a collagen scaffold; ns, not significant. ***p < 0.001.