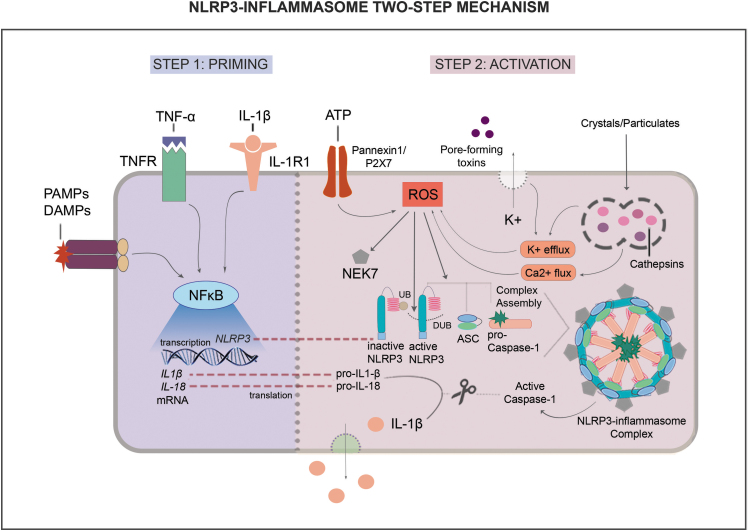
Figure 1.
NLRP3-inflammasome two-step mechanism. The NLRP3 inflammasome is activated through a two-step mechanism. In step 1, called priming, NF-κB signaling is induced by IL-1β, TNF-α, DAMPs, and PAMPs through specific receptors, leading to transcription of NLRP3 components and its effectors IL-1β and IL-18. In step 2, called activation, ATP, pore-forming toxins, crystals/particulates and other cell metabolism stresses induce ROS formation. In turn, ROS contribute to the assembly of active NLRP3, ASC, and pro-caspase-1, inducing NEK7 and deubiquitination of NLRP3. This multiprotein complex then activates caspase-1, which in turn, cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into active IL-1β and IL-18 and these cytokines are then released into extracellular space. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; DUB, deubiquitinase; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-18, interleukin 18; NEK7, NIMA-related kinase 7; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor pyrin domain containing 3; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; UB, ubiquitin.