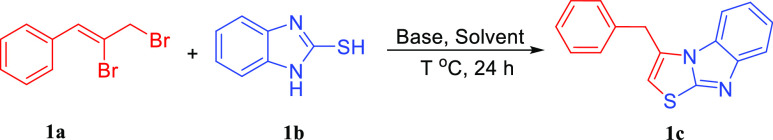
Table 1. Optimization of the Reaction Conditionsa.
| entry | solvent | base | T (°C) | yield (%)b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DMF | Cs2CO3 | 110 | 81 |
| 2 | DMSO | Cs2CO3 | 110 | 68 |
| 3 | toluene | Cs2CO3 | 110 | 12 |
| 4 | 1,4-dioxane | Cs2CO3 | 110 | 36 |
| 5 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 110 | 81 |
| 6 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 100 | 87 |
| 7 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 90 | 93 |
| 8 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 80 | 90 |
| 9 | MeCN | Na2CO3 | 90 | 63 |
| 10 | MeCN | t-BuOK | 90 | 43 |
| 11 | MeCN | 90 | 15 | |
| 12 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 90 | 78c |
| 13 | MeCN | Cs2CO3 | 90 | 90d |
Reaction conditions: 1a (0.3 mmol, 1.0 equiv), 1b (0.3 mmol, 1.0 equiv), and base (0.6 mmol, 2.0 equiv) in solvent (2.0 mL) for 24 h.
The yields were determined by 1H NMR analysis using 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as the internal standard.
Gram-scale (10 mmol scale) reaction.
(3-Bromoprop-1-yn-1-yl)benzene 1e was used.