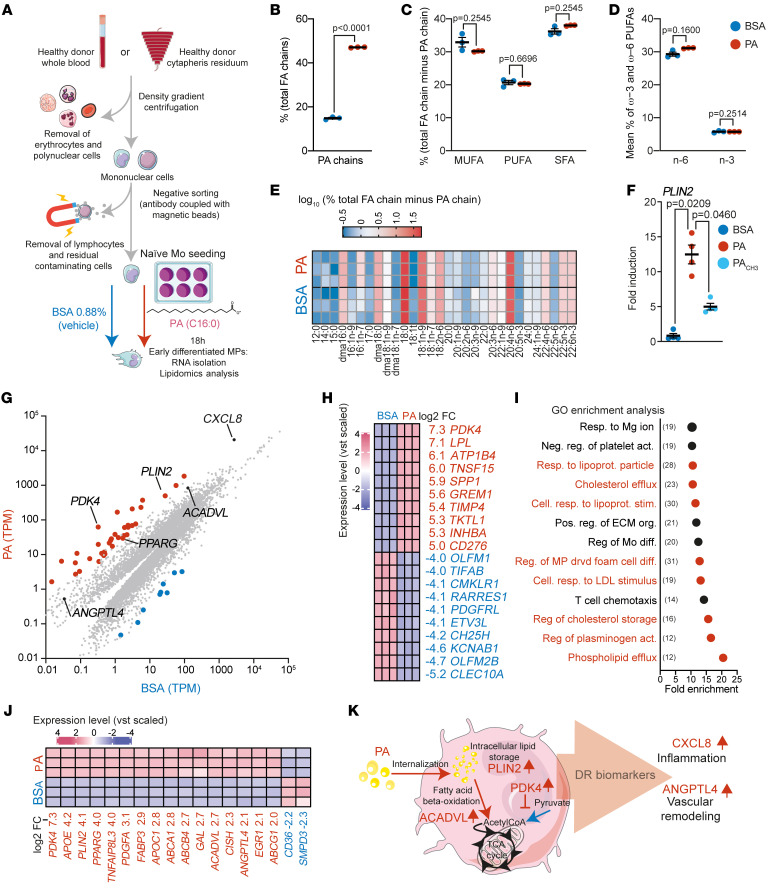
Figure 2. PA stimulation triggers the expression of key DR markers by MPs.
(A) Schematic representation of Mo isolation, treatment, and preparation. (B–D) Chromatographic analysis of FA chain composition after BSA (n = 3) or PA (n = 3) treatment. (B) Mean percentage of PA (C16:0) chains relative to total FAs. P s were calculated using Welch’s t test. (C) Mean percentage of monounsaturated FAs (MUFAs), polyunsaturated FAs (PUFAs), and saturated FAs (SFAs) (minus PA). (D) Mean percentage of ω−3 and ω–6 PUFAs. (C and D) P values were calculated using multiple Welch’s t tests corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Šidák method. (E) Heatmap representation of the percentage of individual FA chains relative to total FA chains (minus PA). (F) RT-qPCR quantification of PLIN2 after treatment with BSA (n = 4), PA (n = 4), or PACH3 (n = 4). P values were determined by 1-way Welch’s ANOVA (P = 0.0021) followed by Dunnett’s T3 multiple-comparison test. (G–I) RNA-Seq transcriptomics analysis after BSA (n = 3) or PA (n = 3) treatment. (G) Scatter plot of the mean TPM value for all transcripts detected after BSA (x axis) or PA (y axis) treatment. The red and blue dots represent transcripts upregulated with a log2 FC of 4 or higher or a log2 FC of 4 or lower. (H) Heatmap representation of the log2 variance stabilizing transformation (vst) of the top 10 upregulated and downregulated transcripts. (I) GO enrichment analysis representing the fold enrichment of the 528 transcripts with a log2 FC of 2 or higher; red dots represent pathways related to lipid metabolism. Numbers in parenthesis represents the number of genes regulated by PA stimulation. Resp., response; Neg., negative; reg., regulator; act. activation; lipoprot., lipoprotein; Cell., cellular; stim., stimulation; Pos., positive; org., organization; diff., differentiation; drvd, derived. (J) Heatmap representation of the log2 vst of transcripts with a log2 FC of 4 or higher and belonging to the GO pathway “fatty acid metabolic process.” (K) Schematic representation of the biological function of the markers selected as a signature of lipid exposure.