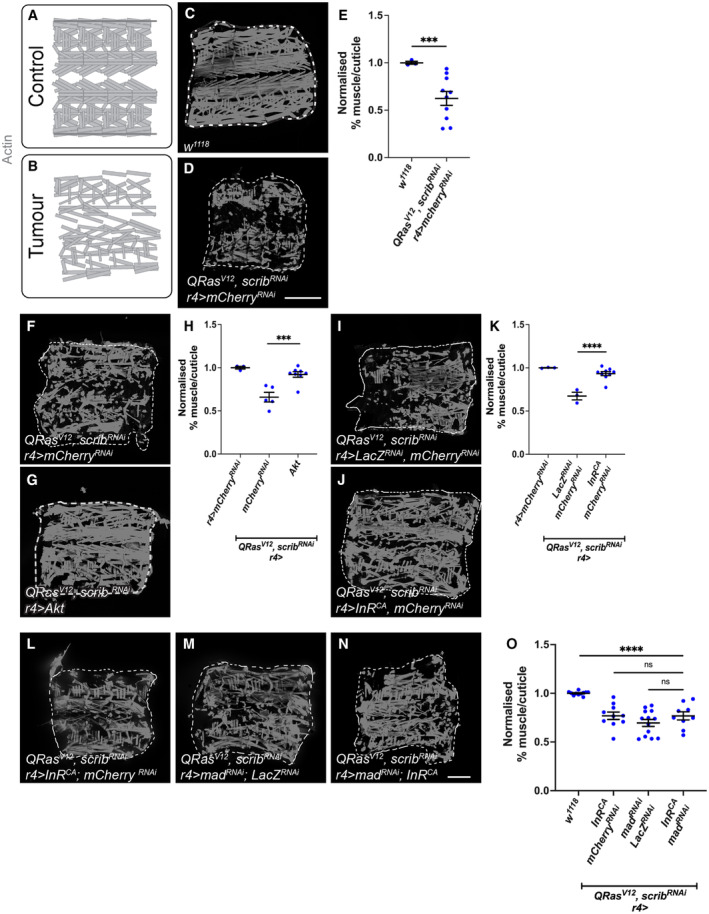
Figure 3. Insulin signalling in the fat body improves muscle integrity in cachectic animals.
-
A, BSchematic depicting intact muscle fillet in control animals, versus deteriorated muscle fillets in tumour animals.
-
C, DMuscle fillets stained with phalloidin (Actin) from w 1118 or QRas V12 scrib RNAi tumour‐bearing animals where mCherry RNAi was expressed in the fat body (r4‐GAL4). Detachments are marked with yellow arrows.
-
EQuantification of normalised muscle detachment in (C, D). w 1118 (n = 3), QRas V12 scrib RNAi (n = 10).
-
F, GMuscle fillets stained with phalloidin (Actin) from QRas V12 scrib RNAi tumour‐bearing animals raised at 25°C, where in the fat body, either mCherry RNAi , or Akt was overexpressed.
-
HQuantification of normalised muscle detachment in (F, G), r4>mCherry RNAi (n = 3). QRas V12 scrib RNAi ; r4>mCherry RNAi (n = 5), QRas V12 scrib RNAi ; r4>Akt (n = 8).
-
I, JMuscle fillets stained with phalloidin (Actin) from QRas V12 scrib RNAi tumour‐bearing animals raised at 25°C, where in the fat body, either lacZ;mCherry RNAi , or InR CA ; mCherry RNAi was overexpressed.
-
KQuantification of normalised muscle detachment in (I, J), r4>mCherry RNAi (n = 3). QRas V12 scrib RNAi ; r4>lacZ;mCherry RNAi (n = 3), QRas V12 scrib RNAi ; r4>InR CA ; mCherry RNAi (n = 9).
-
L–NMuscle fillets of QRas V12 scrib RNAi tumour‐bearing animals raised at 25°C where InR CA ; mCherry RNAi or mad RNAi ; LacZ RNAi or InR CA ; mad RNAi was expressed in the fat body (r4‐GAL4).
-
OQuantification of muscle detachment in (L–N). w 1118 (n = 10), InR CA ; mCherry RNAi (n = 8) or mad RNAi ; LacZ RNAi (n = 14) or InR CA ; mad RNAi (n = 9).
Data information: Scale bar is 200 μm for muscle fillet staining carried out at 7 days after tumour induction. Graphs are represented as Mean ± SEM, n = the number of samples. (***) P < 0.001, (****) P < 0.0001, (ns) P > 0.05. For experiments with two genotypes, two‐tailed unpaired student's t‐tests were used to test for significant differences. The Welch's correction was applied in cases of unequal variances. For experiments with more than two genotypes, significant differences between specific genotypes were tested using a one‐way ANOVA and a subsequent Šidák post‐hoc test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
