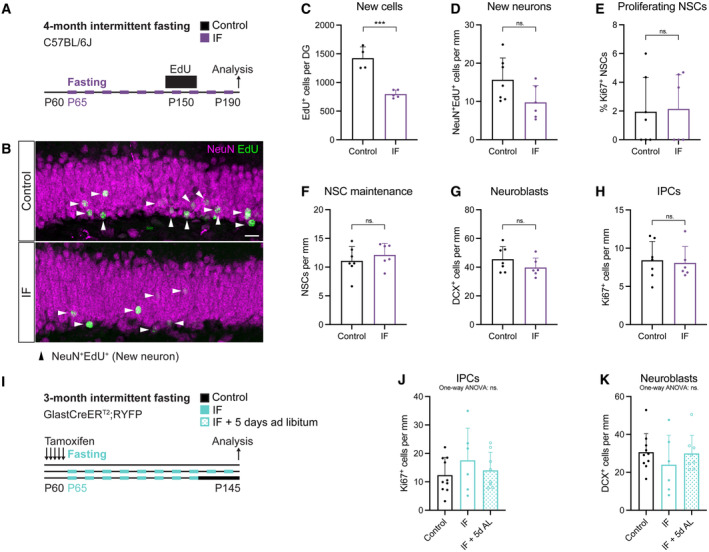
Figure 6. 4 months of every‐other‐day IF do not increase adult neurogenesis.
-
A2‐month‐old male C57BL/6J mice were subjected to 4 months of IF, as in previous studies that reported increases in adult neurogenesis. A survival assay with the thymidine analogue EdU (12‐day labelling—1‐month chase) was used to evaluate neurogenesis.
-
BImage of newly born neurons identified by colocalisation of EdU and the marker for mature neurons NeuN. Arrowheads indicate EdU+NeuN+ cells in this Z‐plane. Some nuclei appear faint because most of their nucleus was located in adjacent Z‐planes. The whole Z‐stack was used for quantification.
-
CStereological quantification of new cells (EdU+ cells) in the whole DG of control and 4‐month IF C57BL6/J mice. 4 months of IF induce a decrease in EdU‐labelled neurons. n control = 4, n IF = 5. Two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, P = 0.0003.
-
DQuantification of new neurons (NeuN+EdU+) normalised to DG length per 40‐μm‐thick section. n control = 7, n IF = 6. Two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, P = 0.0628.
-
E–HQuantification of the percentage of proliferating NSCs (E), and the number of NSCs (F), neuroblasts (G) and IPCs (H) normalised to DG length per 40‐μm‐thick section. The neurogenic lineage is not affected by 4 months of IF. n control = 7, n IF = 6. Two‐tailed unpaired t‐tests; (E) P = 0.8863, (F) P = 0.4324, (G) P = 0.2154, (H) P = 0.7970.
-
I2‐month‐old GlastCreERT2;RYFP mice were subjected to 3 months of IF, after which a subset of IF mice had ad libitum access to food for 5 days.
-
J, KQuantification of IPCs (J) and neuroblasts (K) normalised to DG length per 40‐μm‐thick section in control, IF and IF mice with 5 days of ad libitum eating before analysis. One‐way ANOVAs; n control = 10, n IF = 6, n IF+5dAL = 8; (J) P = 0.4440, (K) P = 0.5120.
Data information: Bars and error bars represent average + s.d.; dots represent individual mice. Significance summary: ns, P > 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. Scale bar: 20 μm.
