Figure EV2. Inhibition of mitochondrial translation with tetracyclines inhibits IRE1α and MAPK signaling, dependent on MALSU1.
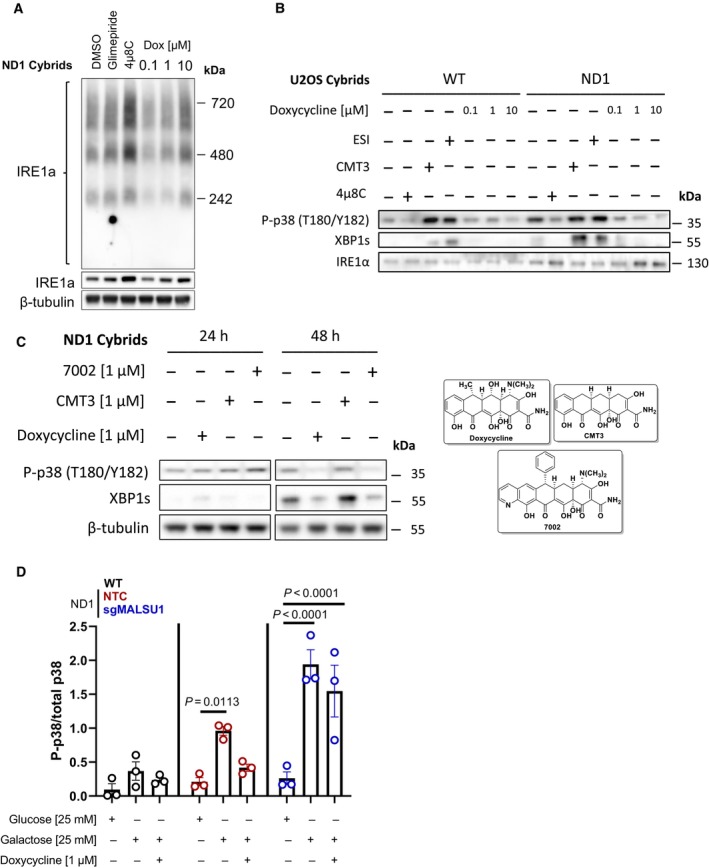
- Whole cell IRE1α oligomerization states under galactose conditions assessed by blue‐native PAGE. BN‐PAGE of IRE1α with whole cell extracts does not capture doxycycline regulation of high‐order oligomers when compared to ER concentrated at the mitochondria (Mito/ER extracts, Fig 4B). Glimepiride (25 μM) and IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8C (20 μM), compounds previously identified to rescue complex I mutants from nutrient deprivation, were used as controls. Note compensatory increase in IRE1α expression and oligomerization in 4μ8C treated cells.
- The activation of p38 MAPK is downstream of IRE1α and can be modulated by ERAD and mitochondrial translation. WT and ND1 cells were cultured in galactose media for 48 h and analyzed for the activation of MAPK and UPR signaling as evidenced by phosphorylation of p38 (P‐p38) and expression of XBP1s, respectively. Pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α with 4μ8C (20 μM) and p97 inhibitor ESI (20 μM) indicate P‐p38 and XBP1s are downstream of IRE1α and can be controlled by ERAD. CMT3 (1 μM) does not affect P‐p38 MAPK or XBP1s levels when compared to doxycycline (1 μM) indicating inhibition of mitochondrial translation, not off target effects of tetracyclines, modulates UPR and MAPK signaling.
- UPR and MAPK signaling are activated after 48 h of galactose stress in ND1 cybrids, where doxycycline (1 μM) and chemically distinct 7002 (1 μM), but not CMT3 (1 μM) attenuate these responses.
- Doxycycline suppresses p38 MAPK phosphorylation depending on MALSU1. Data represents the average ± s.e.m. p38 phosphorylation level normalized to total p38 using western blot densitometry (error bars represent the average ± s.e.m. of n = 3 biological replicates). Statistics across glucose, galactose, and doxycycline treated cultures in WT, ND1, and sgMALSU1 cells was calculated using two‐way ANOVA, multiple comparisons.
