Figure 6. Caf1i (CNOT7/8) inhibitor has anti‐viral activity against HCMV and CCR4‐NOT disruption selectively impacts host mRNA poly(A)‐tails during HCMV infection.
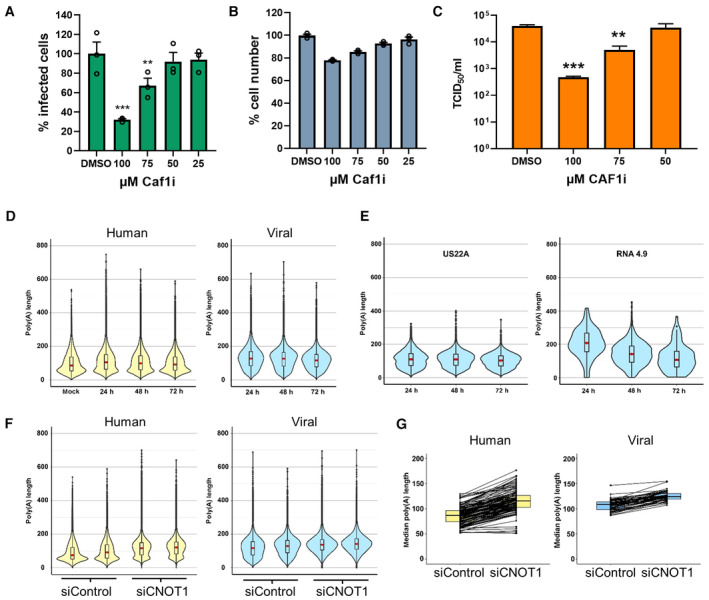
- NHDFs infected with HCMV (AD169) at low MOI (0.05) for 1 h and subsequently incubated for 7 days in the presence of Caf1 inhibitor (Caf1i) or vehicle control (DMSO) equivalent to the highest treatment concentration. Infected cells were identified as in Fig 1A using high content imaging. Mean % infected cells ± SEM, normalized to DMSO‐treated cells (n = 3 biological replicates), is plotted. Statistical significance was established by ANOVA test with Dunnett multiple comparison correction compared with DMSO sample, (**) P < 0.02, (***) P < 0.001, no asterisk: not significant.
- NHDF cell viability following 7 days Caf1i treatment was assessed by quantifying cell number by DAPI nuclear staining and high content imaging. Mean cell number (± SEM) normalized to DMSO‐treated cells (n = 3 biological replicates) is shown.
- Infectious viral titers from culture supernatants following Caf1i treatment were determined by TCID50, plotted as the mean ± SEM (n = 6 biological replicates). Statistical significance was established by ANOVA test with Dunnett multiple comparison correction compared with DMSO sample, (**) P < 0.02, (***) P < 0.001, no asterisk: not significant.
- Poly(A) tail length distributions on host (left, yellow) and viral (right, blue) RNAs from nanopore direct RNA sequencing of mock infected and HCMV infected (24, 48, 72 HPI) NHDFs using Nanopolish.
- Poly(A) tail length distributions of individual HCMV transcripts.
- Poly(A) tail length distributions for host and viral RNAs obtained from HCMV‐infected NHDFs (TB40/E MOI = 3, 72 HPI) treated prior to infection with either a non‐silencing control siRNA or CNOT1 targeting siRNA (#1). Results from two independent experiments are shown adjacently.
- Median poly(A) tail lengths of each host and viral mRNA in (F).
Source data are available online for this figure.
