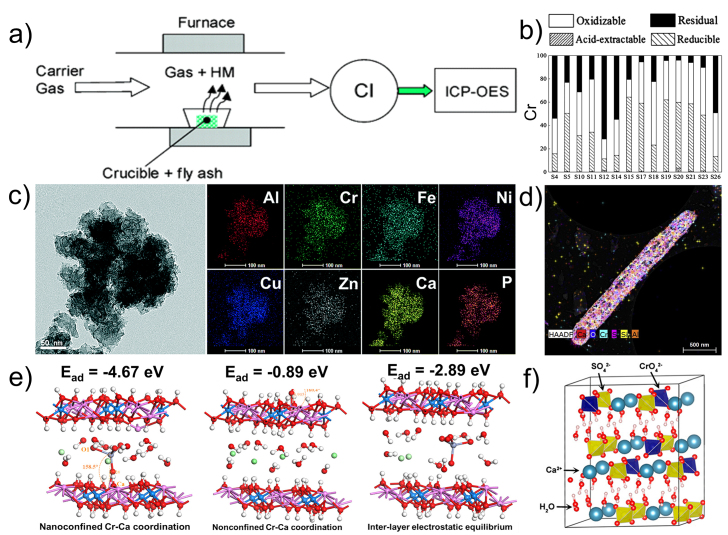
Fig. 7.
The analysis methods of HMSWs. (a) A setup of the online detection for the evaporation of HMs from fly ash by ICP-OES (Reprinted with permission from ref. [132]. Copyright (2004) American Chemical Society); (b) distribution of the different metal fractions in sludge samples (Reprinted with permission from ref. [133]. Copyright (2017) American Chemical Society); (c) the TEM image and elemental maps of the sludge (Used with permission of Royal Society of Chemistry, from ref. [140], permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.); (d) Cs-STEM-XEDS image of the reduced chromite ore processing residue (Reprinted from ref. [141], Copyright (2021), with permission from Elsevier); (e) the binding modes and adsorption energies (Ead) of CrO42− on hydrocalumite (Ca4Al2Cl2(OH)12·6H2O) (Reprinted with permission from ref. [138]. Copyright (2021) American Chemical Society); (f) the crystal structure model of CrO42--encapsulated gypsum sludge (Reprinted with permission from ref. [139]. Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society).