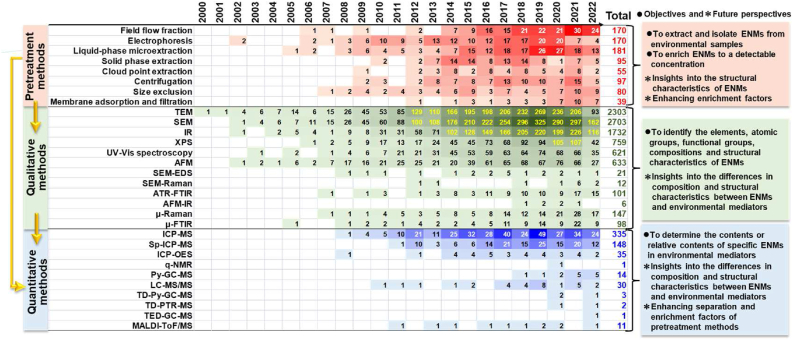
Fig. 3.
Emergence and development timeline of analytical methods that are commonly used for the detection of ENMs. The color of each square represents the number of articles related to the corresponding method, which is the number in the box. The darker the color, the larger the number of related articles. TEM, transmission electron microscopy; SEM, scanning electron microscopy; SEM-EDS, SEM-energy dispersive spectrometer; IR, infrared spectroscopy; AFM, atomic force microscopy; FTIR, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy; ICP-MS, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; Sp-ICP-MS, single-particle ICP-MS; ICP-OES, ICP optical emission spectrometry; q-NMR, quantitative proton-nuclear magnetic resonance; Py-GC-MS, pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography MS/MS; TD-Py-GC-MS, thermal desorption-Py-GC-MS; TD-PTR-MS, TD-proton transfer reaction-MS; TED-GC-MS, thermal extraction-desorption-GC-MS; MALDI-ToF/MS, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.