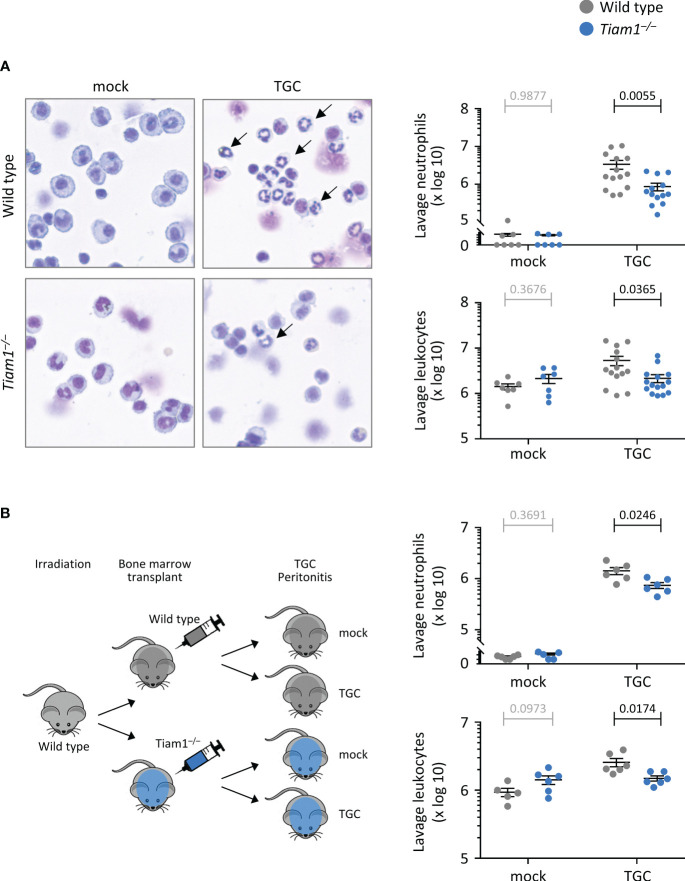
Figure 2.
Tiam1 is required for neutrophil recruitment during aseptic peritonitis, via haemopoietic cell-intrinsic mechanisms. (A) Wild type (grey symbols) and Tiam1–/– (blue symbols) mice were treated i.p. with 0.25 ml thioglycollate (TGC), or mock-treated, and culled 3 h later. Peritoneal lavages were analysed by Kwick-Diff staining of cytospins, and in parallel by flow cytometry, to identify neutrophils (Gr1hi, CD11bhi). Representative images show Kwick-Diff stained cytospins; black arrows show examples of neutrophils. Quantifications shown are from cytospin analysis. Data are mean ± SEM pooled from 4 independent experiments, with 1-3 mock and 3-4 TGC treated mice per experiment; each dot represents one mouse. (B) Irradiated wild type mice received either wild type or Tiam1–/– bone marrow cells, and their haematopoietic system was left to recover for 10 weeks before treatment with TGC and analysis as in (A). Data are mean ± SEM pooled from 2 independent experiments, with 1-3 mock- and 3 TGC-treated mice per experiment; each dot represents one mouse. Statistics in (A, B) are one-way ANOVA on log-transformed data followed by pairwise comparisons with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; p-values in black denote significant differences, p-values in grey are non-significant.