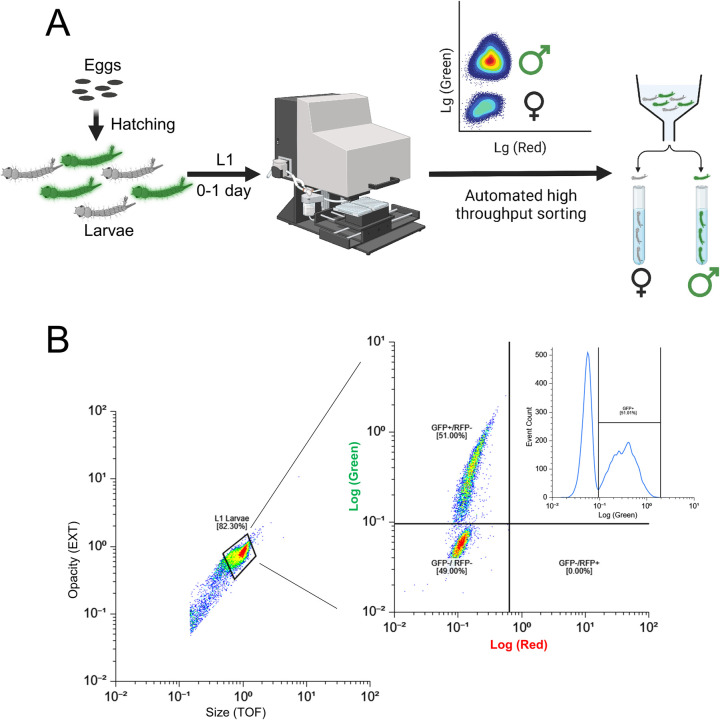
Fig 2. Precise sex-sorting at scale using COPAS.
(A) A schematic diagram of large-scale sex-sorting processes using COPAS is shown. The eggs of transgenic mosquitoes, which have been engineered with the SEPARATOR system, were incubated in a vacuum chamber filled with deionized water to hatch them. 24 hours post-egg hatching, the larvae expressing GFP were screened using the COPAS instrument. The GFP-positive larvae were then carefully sorted, and raised in a controlled environment until they reached adulthood. Once the adults have reached maturity, their sexes were verified through various methods. Figure was created using BioRender. (B) The eggs of transgenic mosquitoes that were genetically engineered to carry the SEPARATOR system were incubated in a vacuum chamber using deionized water. After 24 hours of incubation, the hatched larvae were passed through a COPAS instrument. To ensure accurate sorting, the larvae were selected based on both their opacity and size, and then sorted by the intensity of their GFP expression.