Table 1.
The most important phytochemical compound of A. millefolium.
| No | Compound name | Class of compound | Structure | Effect | Part of plant | Extract/essential oil | Half life | Mechanism of action | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camphene | Monoterpenes | 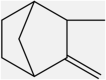 |
Anti-inflammatory, reducing triglyceride level | Leaf | Essential oil | 9.12 days | Prostaglandin e2 inhibition, cyclooxygenase (cox) inhibition. (Fig. 1), Inhibition of MTP |
[15] [33] [34] [35] [36] |
| 2 | α-pinene | Monoterpenes | 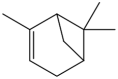 |
Antibacterial, anti inflamatory anti-tumor | Leaf | Essential oil | 1.4 h | inhibit the growth of bacteria, Decrease in inflammatory factors such as TNF-α , down-regulating Cdc25C mRNA and protein expression, |
[15] [33] [37] [38] [39] [36] |
| 3 | β-pinene | Monoterpene | 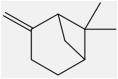 |
Antibacterial, Inhibitory effects on breast cancer and leukemia |
Leaf | Essentia oil | 4.9 h | Decreasing inflammatory factors such as TNF-α | [15] [33] [36] |
| 4 | Limonene | Monoterpene | 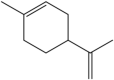 |
anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective | Leaf | Essential oil | 12–24 h | Reducing no production and nerve activation, thus reducing neuron cell (Fig. 2) | [40] [41] [42] [36] |
| 5 | Camphor | Terpenoid ketones |  |
Antitussive, analgesic, nasal decongestant | Leaf | Essential oil | 4–8 h | reducing TRPA1-mediated cough, Activating heat-sensitive trpv1 and trpv3 receptors | [33] [43] [44] [45] [46] [36] |
| 6 | 1,8-cineole | Monoterpene | 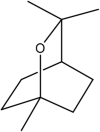 |
Anti-inflammatory Antioxidant effects |
Leaf | Essential oil | 6.7 min | Induced enzymatic and nonenzymatic cellular antioxidants and metabolic phase ii detoxifying enzymes | [33] [47] [48] [36] |
| 7 | Linalool | Monoterpenoid | 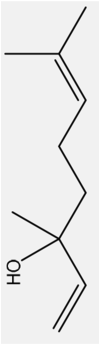 |
, decrease anxiety, sedative effects, Hepatoprotective, dermal sensitizer | Leaf | Essential oil | 3.2 h | A competitive antagonist of glutamate, and as a non-competitive antagonist of NMDA receptors in brain cortical membranes | [33] [49] [50] |
| 8 | Luteolin | Flavonoid | 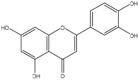 |
, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory | Whole Plant | Essential oil/extract | Less than 5 h | inhibited cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 and/or G2/M cell cycle arrest, Binding to the thromboxane a2 receptor | [51] [52] [53,54] |
| 9 | Isochlorogenic acid | Polyols | 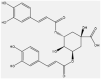 |
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory | Leaf | Extract | 227∼292 min | High restoration of glutathione levels | [55] [56] [53] [57] |
| 10 | Apigenin | Estrogenic flavonoid | 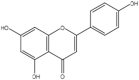 |
An antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | Whole Plant | Extract | 91.8 h | oxidant enzymes inhibition, modulation of redox signaling pathways (NF-kB, Nrf2, MAPK, and P13/Akt), Regulating a p53-bax-caspase-3 apoptotic pathway | [58] [59] [60] [53] [61] |
| 11 | Kaempferol | Flavonoid | 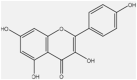 |
Anti-inflammatory, anticancer | Water extract | 2.93–3.79min | Cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, inducing apoptosis | [62] [63] [36] |
|
| 12 | Caffeic acid | Phenolic glycoside | 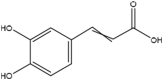 |
Hepatoprotective, anticarcinogenic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | Whole plant | Extract | 0.14 h | Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and shielding against ldl oxidation (Fig. 3) | [64] [65] [66] [67] [68] |
| 13 | Quercetin | f | 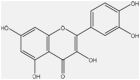 |
Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial | Whole plant | Extract | 3.5 h | Inhibiting lipopolysaccharide (lps)-induced tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) production in macrophages | [65] [69] [70] |
| 14 | Betonicine | Alkaloids | 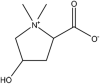 |
Positive effect on digestive system and the blood stream | Whole plant | Extract | N.m | Not explored | [71] [72] |
*N.E: Not explored.
