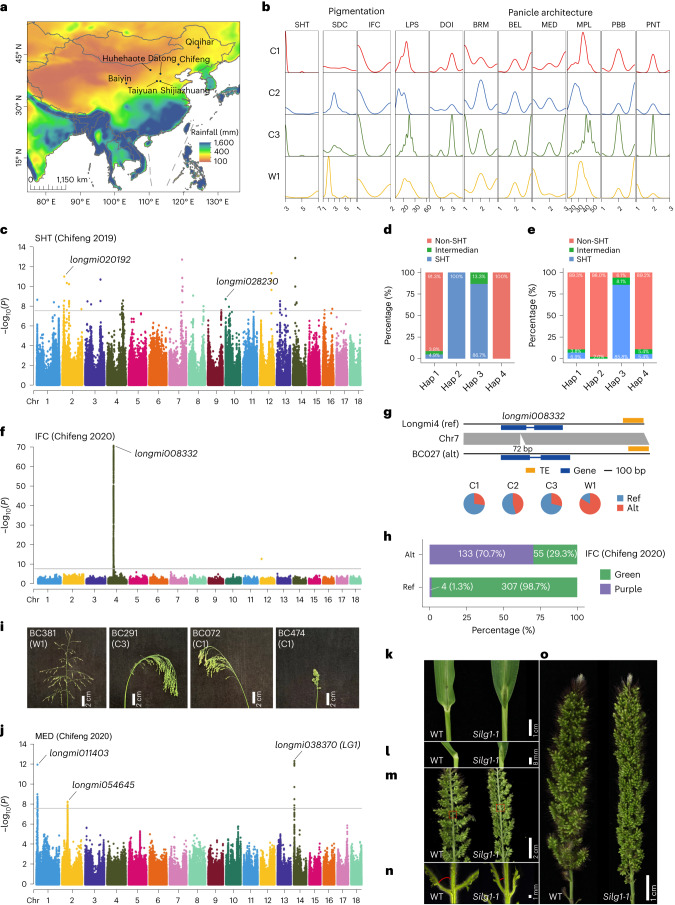
Fig. 5. GWAS of genomic variations associated with domestication and agronomically important traits in broomcorn millet.
a, Location of seven sites used for phenotype evaluation. The colors represent the yearly rainfall. The geographical map was obtained from ArcGIS (https://www.arcgis.com/index.html). The yearly rainfall data were obtained from WorldClim (https://www.worldclim.org/). b, Distribution of SHT, seed and inflorescence (colors), and panicle architecture traits in broomcorn millet. SHT, SDC, IFC, length of panicle stem (LPS), DOI, the branch of the ear of grain and main shaft drift angle (BRM), the branch of ear length (BEL), MED, main panicle length (MPL), projection on branch base (PBB) and PNT are shown. Details of the traits are described in Supplementary Table 19. c, Manhattan plot of the GWAS of seed SHT based on the Chifeng 2019 phenotype. d,e, SHT phenotype of four Haps of longmi020192 (d) and longmi028230 (e). In d, the numbers of accessions with the Hap 1, 2, 3 and 4 Haps were 446, 26, 15 and 12, respectively. In e, the numbers of accessions with the Hap 1, 2, 3 and 4 Haps were 318, 99, 49 and 37, respectively. f, Manhattan plot of GWAS of IFC based on the phenotype collected from Chifeng in 2020. g, Comparisons of BC027 and Longmi4 sequences with a 72-bp insertion at the longmi008332 locus. h, Distribution of IFC in Ref and Alt alleles. i, Panicles of the representative accessions of wild and cultivated broomcorn millet. j, Manhattan plot of the GWAS of MED based on the phenotype collected from Chifeng in 2020. k–o, Phenotypic analyses of ligule (k,l) and panicle traits (m–o) of the lg-1 mutant and WT plants. The horizontal lines in c,f,j depict the significance threshold (P = 2.64 × 10−8 or −log10(P) = 7.58), which was set at 0.05/n (n represents the total number of SNPs).