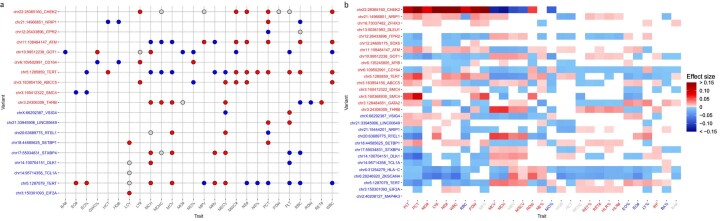
Extended Data Fig. 6. Effects of CH GWAS variants on clinical hematology parameters.
a, GWAS Catalog reports: For each sentinel CH GWAS variant, we identified all variants in LD with r2 > = 0.8 within +/−500kb. For those variants, we searched the GWAS Catalog for reported associations with P-values < 1 × 10−7 from linear regression association. CH GWAS loci (y-axis) are colored red if the Alt allele increased CH risk, otherwise blue. Circles are colored red if the Alt allele was associated with an increase in the hematological trait value (x-axis), blue if there was a decrease and gray if the direction of effect could not be ascertained. b, Associations from linear regression between sentinel CH GWAS variants and clinical hematology traits measured on contemporaneous samples in the UKB: CH GWAS loci (y-axis) are colored red if the Alt allele increased CH risk, otherwise blue. Hematological trait symbols (x-axis) are colored red if their values increased in association with the CH phenotype, blue if they decreased in CH and gray if they were not associated with CH. Blocks are colored in if the effect of the CH GWAS variant on the trait was at least nominally significant: red indicates that the Alt allele was associated with an increase in the hematological trait value, blue indicates a decrease. Intensity of color indicates the effect size. Hematological traits are ordered by hierarchical clustering within the CH at-risk and CH protective strata. Platelet parameters were affected by the greatest number of variants: PCT, PLT, PDW and MPV; followed by erythrocytic parameters MCH, RBC and MCV. The best alignments in direction of effects (that is where the effects of the variant on CH and the hematological trait were consistent with the phenotype:phenotype association) were seen again for platelet parameters PDW, PCT and PLT as well as for MO#, LY# and BA%. From the perspective of the CH GWAS variants, the variants affecting the most hematological traits were chr6:CD164 and chr6:HLA-C. However chr6:CD164 had rather poor alignment in the direction of effects. The best alignments were seen for chr21:14966851 NRIP1, chr3:THRB and chr3:16068930:SMC4. Clinical hematology parameters are as defined in Sheard47.