FIG. 4.
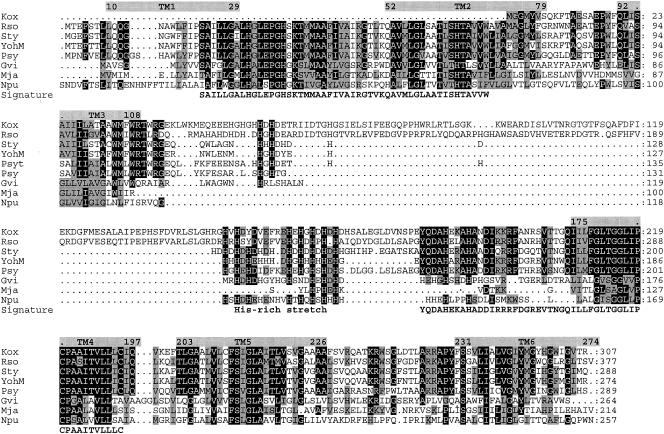
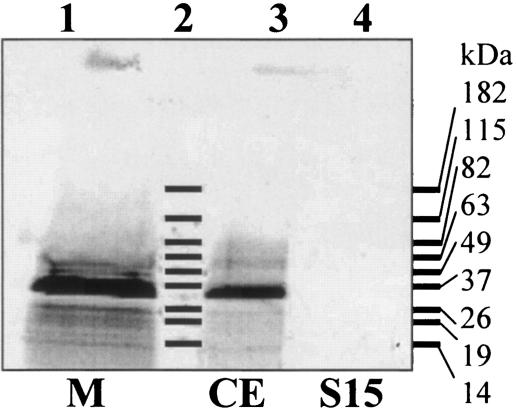
Sequence alignment and topology of YohM and putative open reading frames. (Top) YohM, E. coli (accession number P76425); Sty, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 (accession number NP_461941.1); Psyt, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato strain DC3000 (AAO57731.1); Psy, Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae B728a (ZP_00127113.2); Kox, Klebsiella oxytoca, NirC (AAR82965.1); Rso, Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 (NP_522113.1); Gvi, Gloeobacter violaceus PCC 7421 (NP_926273.1); Npu, Nostoc punctiforme (ZP_00108926.1); and Mja, Methanocaldococcus jannaschii DSM 2661 (NP_248085.1). Amino acid residues at any position that are identical in at least 60% of the sequences throughout the alignment are shaded in black, and residues exhibiting similarity in at least 60% or more of the sequences are shaded in grey. Hydropathy profile analysis predicted six transmembrane helices (grey rectangles above sequences). Numbers indicate coordinates of the amino acids flanking each transmembrane segment (TM). TM3 and TM4 are separated by a 70-amino-acid-long domain encompassing the histidine-rich region of YohM. Signature line indicates the two motifs which are signatures of the YohM family; these motifs were generated by using the MEME and MAST programs (1). (Bottom) In vivo specific labeling of YohM. Strain B834 harboring pAR02T (yohM in pET30 [Novagen]) was grown in the presence of [35S]Met. Cellular fractions were analyzed by SDS-15% PAGE and autoradiography. Lane 1, membrane fraction (M); lane 2, molecular weight; lane 3, crude extract (CE); and lane 4, soluble fraction (S15).