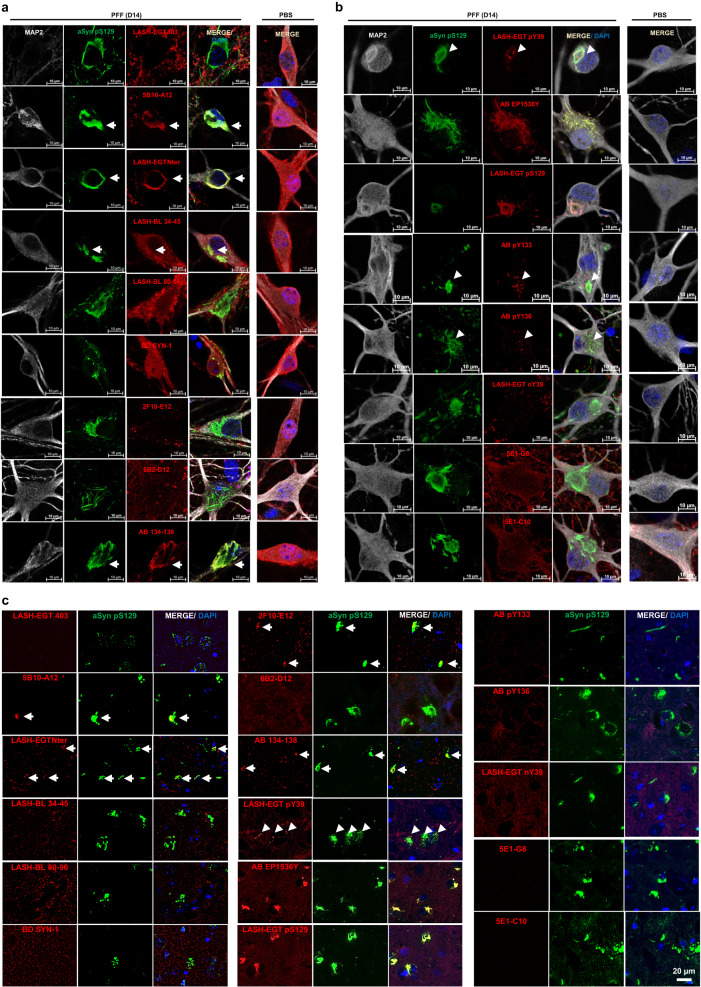
Fig. 6. Application of the aSyn antibodies to the cellular and animal seeding models to profile the newly formed aSyn aggregates.
WT hippocampal neurons were seeded with PFFs for 14 days, and the newly formed aggregates monitored by ICC using the mouse-reactive a non-modified aSyn and b aSyn PTM antibodies in parallel to aSyn pS129 antibodies BL 81A or AB MJF-R13. c The same type of screening was run in PFF-injected mouse amygdala tissues by IHC. The non-modified aSyn antibody signals overlapping with the aSyn pS129-positive aggregates are marked with an arrow. The punctate positivity shown by aSyn pY39, pY133, and pY136 antibodies in close proximity to aSyn pS129-positive aggregates are shown by arrowheads. Note the non-specific diffuse positivity revealed by the two monoclonal nY39 antibodies 5E1-G8 and 5E1-C10 in the WT hippocampal neurons are also revealed in the aSyn KO neurons using these two antibodies (Supplementary Fig. 4A, B). aSyn alpha-synuclein, DAPI 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, ICC immunocytochemistry, IHC immunohistochemistry, KO knockout, MAP2 microtubule-associated protein 2, PBS phosphate-buffered saline, PFF pre-formed fibril, PTM post-translational modification, WT wild-type.